- Halothane enhances GABA activity, causing CNS depression and smooth muscle relaxation.
- It is an inhalation anesthetic used for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia.
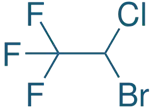
Chemical Formula:
- C₂HBrClF₃
Mechanism of Action:
- Potentiates GABA-A and glycine receptor activity
- Inhibits NMDA receptors and neuronal excitability
- Alters membrane fluidity via interaction with lipid bilayer
Uses:
- Induction and maintenance of anesthesia
- Historically used in pediatric anesthesia
Side Effects:
- Halothane hepatitis (rare but severe hepatic necrosis)
- Cardiac arrhythmias due to sensitization to catecholamines
- Hypotension (vasodilation)
- Bradycardia
- Malignant hyperthermia (when used with succinylcholine)
SAR of Halothane:
-
Halogenated ethane structure:
- Contains three fluorine atoms and one bromine and chlorine.
- The halogens influence potency, lipid solubility, and stability.
-
Lipophilicity:
- Increased fluorination improves CNS penetration and anesthetic potency.
-
Br atom:
- Contributes to molecular weight and affects cardiac sensitization.
-
Asymmetry:
- Causes chirality; racemic mixture used.
-
Metabolic liability:
- Can undergo oxidative metabolism → formation of trifluoroacetyl halide → hepatotoxicity risk.
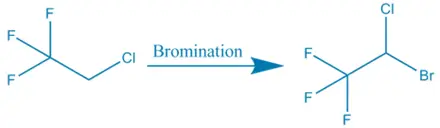
Synthesis of Halothane:
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos