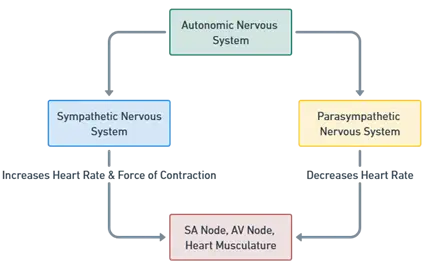
- Heartbeat Regulation by the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)) plays a crucial role in regulating the heartbeat and maintaining cardiovascular homeostasis.
- The ANS consists of two primary branches: the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), both of which have opposing effects on heart function.
-
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
-
Role:
- Responsible for the “fight or flight” response, preparing the body to react to stress or danger.
-
Mechanism:
- The SNS releases neurotransmitters like norepinephrine, which bind to beta-adrenergic receptors on cells in the SA node, AV node, and myocardium.
- This binding:
- Increases the rate of electrical impulse generation by the SA node (increases heart rate).
- Speeds up the conduction of impulses through the AV node.
- Enhances the force of ventricular contractions (contractility).
-
Effects:
- Increased heart rate (tachycardia).
- Stronger heart contractions to meet the body’s increased demand for oxygen and nutrients during stress or physical activity.
Advertisements
-
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS)
-
Role:
- Responsible for the “rest and digest” response, promoting relaxation and energy conservation.
-
Mechanism:
- The vagus nerve (cranial nerve X), the primary nerve of the PNS, releases acetylcholine, which binds to muscarinic receptors on the cells in the SA node and AV node.
- This binding:
- Decreases the rate of electrical impulse generation by the SA node (slows heart rate).
- Reduces the speed of impulse conduction through the AV node.
-
Effects:
- Decreased heart rate (bradycardia).
- Reduced force of heart contractions, conserving energy during periods of rest and recovery.
Balance Between SNS and PNS
- The heart’s rate and force of contraction are determined by the balance between the SNS and PNS.
- Both systems continuously modulate heart activity to adapt to the body’s needs, whether responding to stress, exercise, or rest.
- Factors such as physical activity, emotional state, hormones, and blood pressure influence the balance between the SNS and PNS, adjusting heart function accordingly.