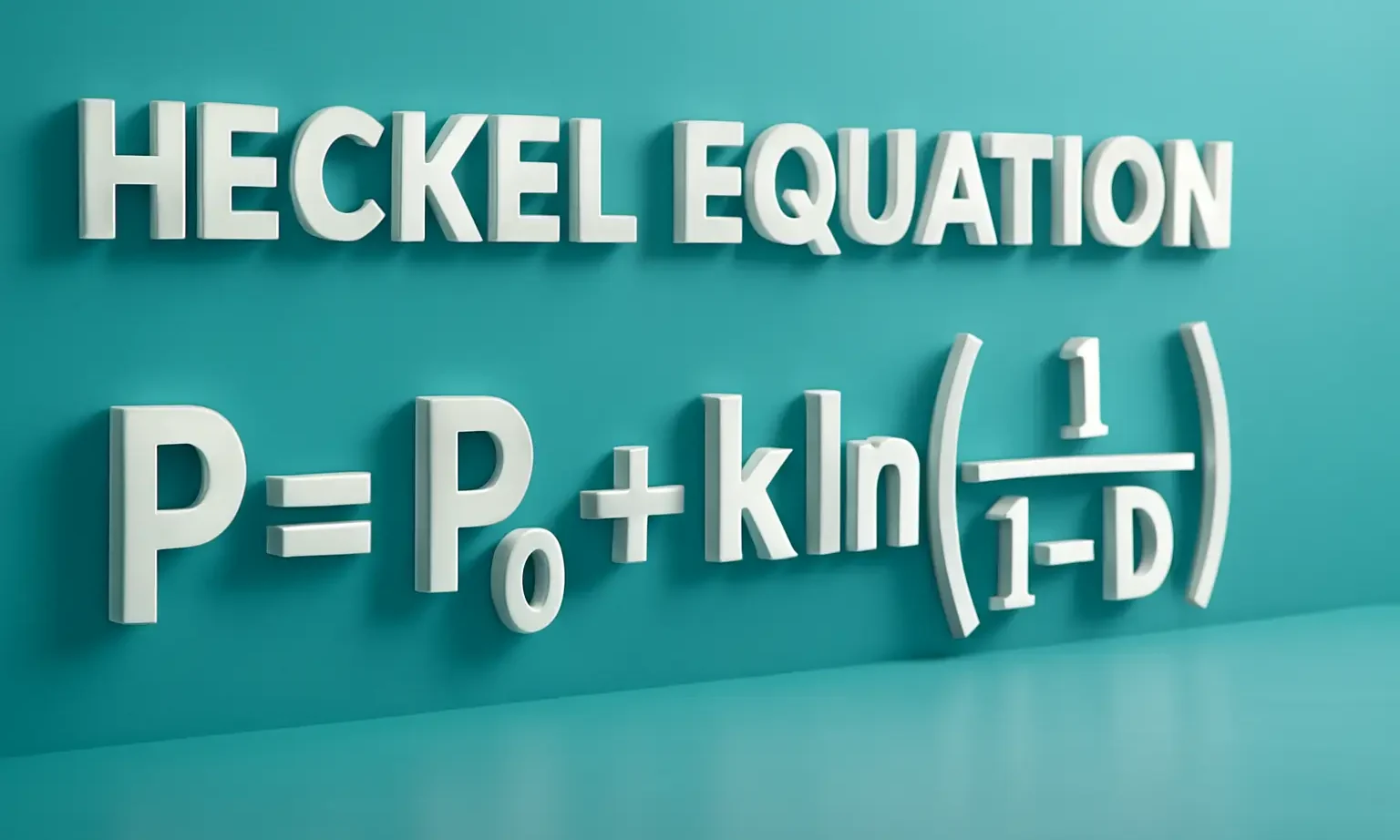Purpose of Heckel Equation:
- The Heckel equation is used to study the compressibility and deformation behavior of powders during tableting.
- It relates porosity reduction to applied pressure and helps identify whether a material deforms plastically or elastically under compression.
Equation:
$\ln\!\left(\tfrac{1}{1-D}\right) = KP + A$
Advertisements
- Where:
- D = relative density of the powder (i.e., density of compact / true density)
- P = applied pressure
- K = slope of the linear portion (related to plasticity)
- A = intercept (related to initial packing)
Interpretation:
- The slope KKK is inversely related to the yield pressure of the material.
- $P_y = \frac{1}{K}$
- Lower Py → greater plasticity.
- Higher Py → more elastic or brittle behavior.
- The intercept AAA provides insight into particle rearrangement at low pressure.
Advertisements
Heckel Plot:
- A plot of $\ln\!\left[\frac{1}{1-D}\right]$ versus pressure.
- Linear region represents plastic deformation.
- Nonlinear regions at the beginning reflect particle rearrangement and fragmentation.
Application of Heckel Equation:
- Used to compare the compressibility profiles of excipients and drug substances.
- Helps in formulation development and predicting tabletability.
Advertisements