- hyperbilirubinemia (excess bilirubin in the bloodstream) and jaundice (the yellow discoloration resulting from that excess), emphasizing the underlying cause and its visible clinical manifestation together.
Hyperbilirubinemia:
Definition:
- Hyperbilirubinemia is characterized by an elevated concentration of bilirubin in the bloodstream. It arises due to either:
-
Increased Bilirubin Production:
- Occurs
- hyperbilirubinemia (excess bilirubin in the bloodstream) and jaundice (the yellow discoloration resulting from that excess), emphasizing the underlying cause and its visible clinical manifestation together.
- when there is excessive breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), leading to higher levels of bilirubin.
-
Decreased Bilirubin Clearance:
- Caused by impaired liver function or bile flow obstruction, reducing the liver’s ability to process and excrete bilirubin.
-
Jaundice
Definition:
- Jaundice is the clinical manifestation of hyperbilirubinemia.
- It is characterized by the yellowish discoloration of the skin, eyes (sclera), and mucous membranes due to the accumulation of bilirubin.
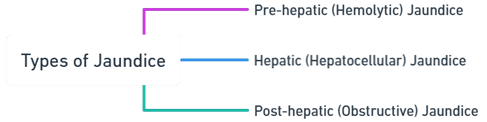
Types of Jaundice
- Jaundice is classified based on the underlying cause into three main types:

Advertisements
-
Pre-hepatic (Hemolytic) Jaundice:
- Cause: Excessive breakdown of red blood cells.
- Characteristics: Elevated levels of unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin.
- Conditions: Hemolytic anemias, autoimmune diseases, infections.
-
Hepatic (Hepatocellular) Jaundice:
-
Post-hepatic (Obstructive) Jaundice:
- Cause: Obstruction in the bile ducts, preventing bilirubin excretion.
- Characteristics: Elevated levels of conjugated bilirubin, possible bilirubin leakage back into the bloodstream.
- Conditions: Gallstones, bile duct or pancreatic tumors, inflammation.
Diagnosis of Jaundice
- Diagnosing jaundice involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests:
-
Medical History and Physical Examination:
- To assess symptoms and identify potential underlying causes of jaundice.
-
Laboratory Tests:
- Blood tests to measure total, direct (conjugated), and indirect (unconjugated) bilirubin levels.
-
Further Diagnostic Tests:
- Liver function tests, imaging studies (e.g., ultrasound, CT scans), and possibly a liver biopsy to determine the precise cause of jaundice.
-
Treatment of Jaundice
- The treatment for jaundice depends on addressing its underlying cause:
-
Medications:
- To treat infections, reduce bilirubin levels, or manage liver conditions.
-
Blood Transfusions:
- In cases of severe hemolytic anemia, where there is excessive destruction of RBCs.
-
Surgical Interventions:
- To remove obstructions in the bile ducts or treat tumors causing post-hepatic jaundice.
-