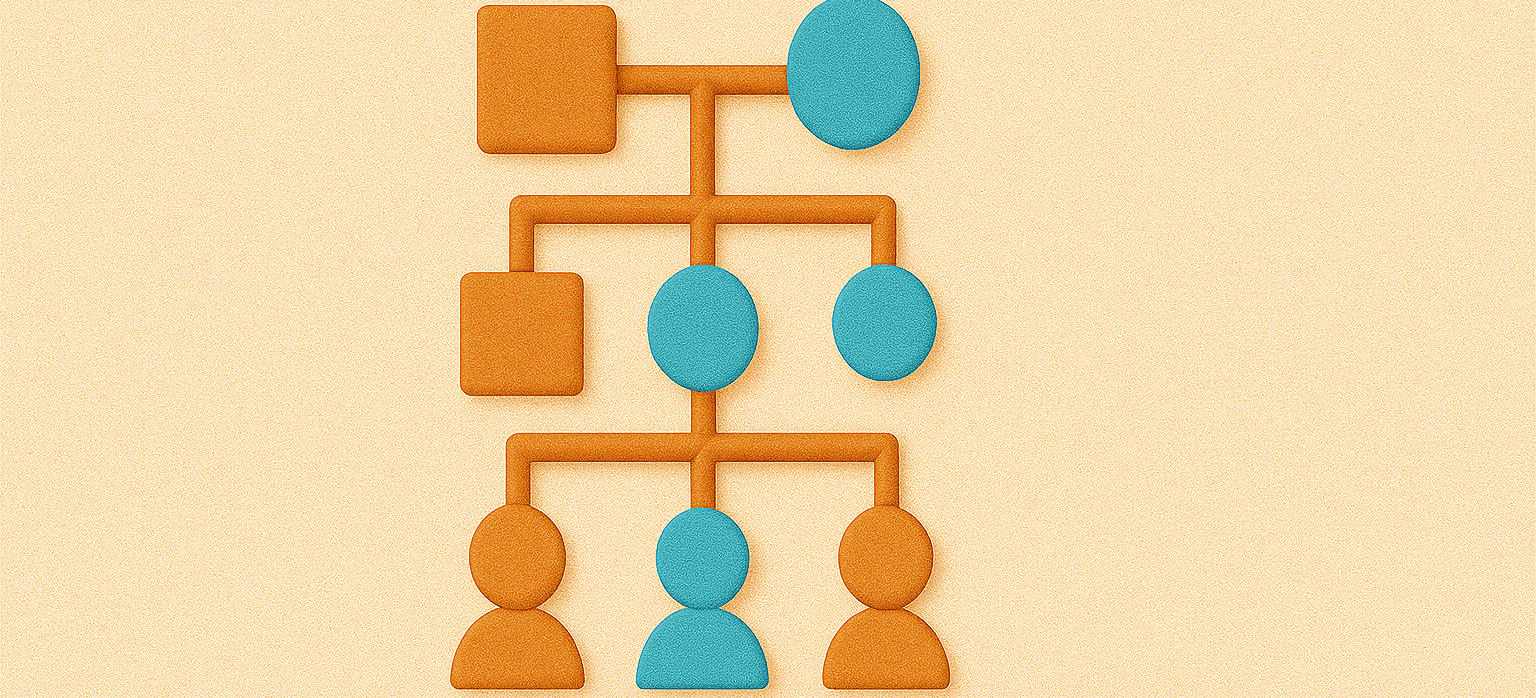Inheritance patterns explain how traits are passed from parents to offspring. These patterns are governed by Mendelian and non-Mendelian principles.
Mendelian Inheritance
Overview:
- Based on Gregor Mendel’s experiments with pea plants.
- Involves traits controlled by single genes on autosomal chromosomes.
Key Laws:
-
Law of Segregation:
- Each individual has two alleles per gene, one from each parent, which separate during gamete formation.
-
Law of Independent Assortment:
- Alleles of different genes assort independently during gamete formation, creating various allele combinations.
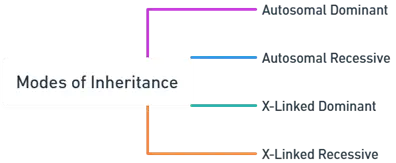
Modes of Inheritance:
Advertisements
-
Autosomal Dominant:
- A single dominant allele causes the trait.
- Offspring have a 50
-
Autosomal Recessive:
- Two recessive alleles are required to express the trait.
- Offspring have a 25
-
X-Linked Dominant:
- Affects the X chromosome.
- Males have a 50
-
X-Linked Recessive:
- More common in males (one X chromosome).
- Females need two copies of the recessive allele to express the trait.
Advertisements
Non-Mendelian Inheritance
Overview:
- Involves complex genetic interactions that don’t follow Mendel’s laws.
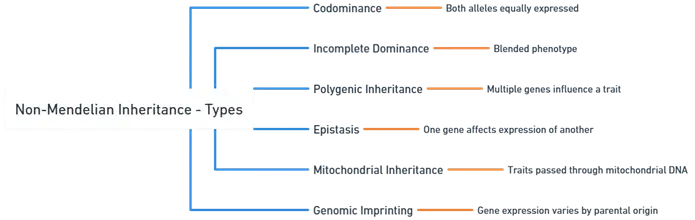
Types:
-
Codominance:
- Both alleles are equally expressed (e.g., AB blood type).
Advertisements -
Incomplete Dominance:
- Neither allele is dominant, resulting in a blended phenotype (e.g., red + white flowers = pink).
-
Polygenic Inheritance:
- Multiple genes contribute to a single trait (e.g., skin color, height).
-
Epistasis:
- One gene’s expression is affected by another gene.
-
Mitochondrial Inheritance:
- Traits passed via maternal mitochondrial DNA.
-
Genomic Imprinting:
- Gene expression varies based on whether the gene is inherited from the mother or father due to epigenetic modifications.
Advertisements