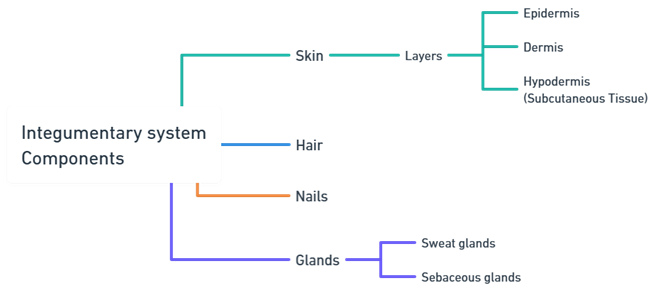
- The integumentary system includes the skin, hair, nails, and glands, playing a crucial role in protection, sensation, temperature regulation, and more.
Key Components of Integumentary System
Skin
- The largest organ, with three layers:
- Epidermis: Outermost layer, protective barrier, contains melanocytes for skin color and UV protection.
- Dermis: Middle layer with connective tissue, blood vessels, nerve endings, hair follicles, and glands.
- Hypodermis: Deepest layer, mainly fat, provides insulation and cushioning.
Advertisements
Hair
- Made of keratin, provides protection, insulation, and sensory input.
Nails
- Keratin structures that protect fingertips and enhance the ability to grasp objects.
Glands
- Sweat Glands: Regulate temperature through sweat.
- Sebaceous Glands: Produce sebum, moisturizing the skin and hair.
- Ceruminous Glands: Produce earwax, protecting the ear.
Functions
- Protection: Shields against injury, pathogens, and UV radiation.
- Sensation: Detects touch, temperature, and pain.
- Temperature Regulation: Manages heat through sweat and blood vessel adjustments.
- Excretion: Removes waste via sweat.
- Vitamin D Synthesis: Produces vitamin D with sunlight exposure.
- Immune Defense: Hosts immune cells to combat pathogens.
Overall, the integumentary system is vital for protecting the body, maintaining balance, and interacting with the environment.
Advertisements