- Ketamine Hydrochloride blocks NMDA receptors, producing dissociative anesthesia with analgesia.
- It is used for anesthesia, pain relief, and emergency sedation.
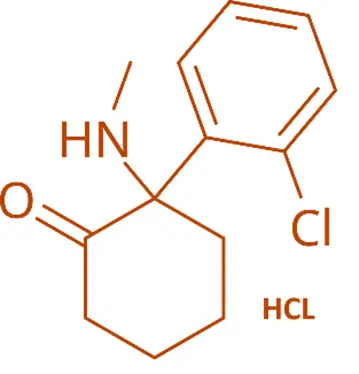
Chemical Formula:
- C₁₃H₁₆ClNO·HCl
Mechanism of Action:
- NMDA receptor antagonist
- Also interacts with opioid, monoaminergic, and muscarinic receptors
- Increases sympathetic output → ↑ BP, HR, CO
Advertisements
Uses of Ketamine Hydrochloride:
- Induction of anesthesia
- Short surgical procedures
- Pediatric and battlefield anesthesia
- Treatment-resistant depression (IV or nasal)
Side Effects of Ketamine Hydrochloride:
- Emergence delirium, hallucinations
- Increased ICP, BP, HR
- Nystagmus, muscle rigidity
- Hypersalivation
SAR of Ketamine:
-
Arylcyclohexylamine structure:
- Essential for NMDA antagonism.
- Phenyl ring increases lipophilicity and CNS activity.
-
Chiral center:
- (S)-ketamine is more potent than (R)-ketamine.
-
Cyclohexanone ring:
- Maintains proper orientation for NMDA receptor binding.
-
Amino group on side chain:
- Allows for water solubility as hydrochloride salt.
-
Lipophilic aryl ring:
- Crucial for CNS penetration and rapid onset.
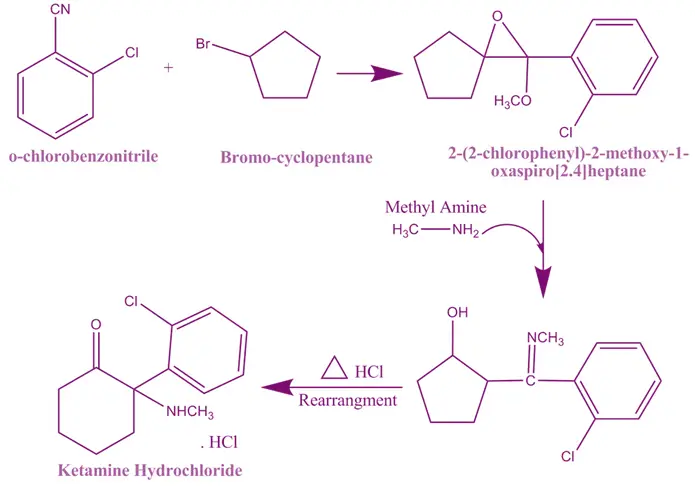
Synthesis of Ketamine:
Advertisements