L-Thyronine is a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone T3 used to treat hypothyroidism and support healthy metabolism.
Structure of L-Thyronine
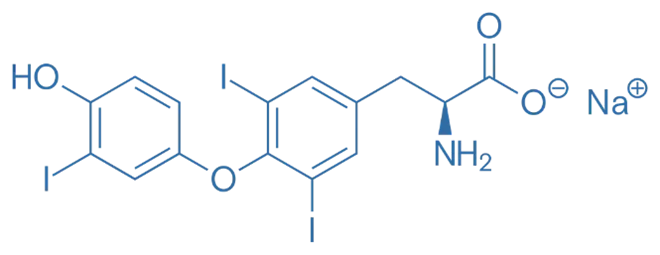
- L-Thyronine, also known as triiodothyronine (T3), is a thyroid hormone with a tyrosine backbone and three iodine atoms.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₇H₁₅I₃NO₄
Mode of Action
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement: Acts similarly to endogenous T3, binding to thyroid hormone receptors and regulating gene transcription.
- Metabolic Enhancement: Increases basal metabolic rate, enhances lipolysis, and promotes thermogenesis.
- Growth and Development: Critical for normal growth, neurological development, and differentiation in tissues.
- Cardiovascular Effects: Increases heart rate, cardiac contractility, and enhances cardiac output.
Uses
- Hypothyroidism: Used when rapid thyroid hormone action is required or in cases where T4 conversion to T3 is impaired.
- Myxedema Coma: Emergency treatment of severe hypothyroidism alongside L-Thyroxine.
- Goiter: Manages thyroid enlargement by providing negative feedback on TSH secretion.
- Thyroid Cancer: As part of adjuvant therapy to suppress TSH and inhibit tumor growth.
- Research: Employed in studies on thyroid hormone physiology and metabolism.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos

