L-Thyroxine is a synthetic thyroid hormone used to treat hypothyroidism by restoring normal metabolism and energy levels.
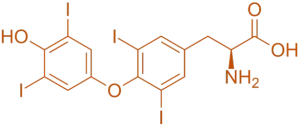
Structure of L-Thyroxine
- It is also known as levothyroxine, is a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) with a tyrosine backbone and four iodine atoms.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₈H₁₉I₄NO₄
Mode of Action
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement: Mimics endogenous thyroxine, binding to thyroid hormone receptors in the nucleus of target cells.
- Metabolic Regulation: Enhances basal metabolic rate by increasing oxygen consumption and heat production.
- Growth and Development: Essential for normal growth, neurological development, and differentiation in various tissues.
- Cardiovascular Effects: Increases heart rate, cardiac contractility, and enhances cardiac output.
Uses
- Hypothyroidism: Replaces deficient thyroid hormones to restore normal metabolic function.
- Myxedema Coma: Emergency treatment of severe hypothyroidism with life-threatening symptoms.
- Goiter: Manages thyroid enlargement by providing negative feedback on thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) secretion.
- Thyroid Cancer: As part of adjuvant therapy to suppress TSH and inhibit tumor growth.
- Scholarly Use: Employed in studies investigating thyroid hormone physiology and metabolism.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos