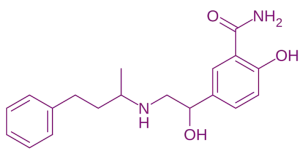
- Labetalol is a dual-action adrenergic antagonist used primarily as an antihypertensive agent.
- It blocks both α1-adrenergic receptors and β-adrenergic receptors (non-selective β-blocker with selective α1-blocking activity).
Chemical Structure & Formula:
- Unique among beta blockers, it contains dual-acting structural features (aromatic rings and a secondary amine) that allow it to block both beta and α₁ receptors.
- Approximate Formula: C₂₀H₂₅NO₃

Mechanism of Action:
- Non selectively blocks β receptors and antagonizes α₁ receptors.
- Beta blockade reduces heart rate and contractility, while α₁ blockade induces peripheral vasodilation, collectively lowering blood pressure without marked tachycardia.
Side Effects of Labetalol:
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Dizziness
- Occasional nausea
Advertisements
Clinical Uses of Labetalol:
- Frequently used in hypertensive emergencies and in managing pregnancy-induced hypertension due to its balanced hemodynamic profile.