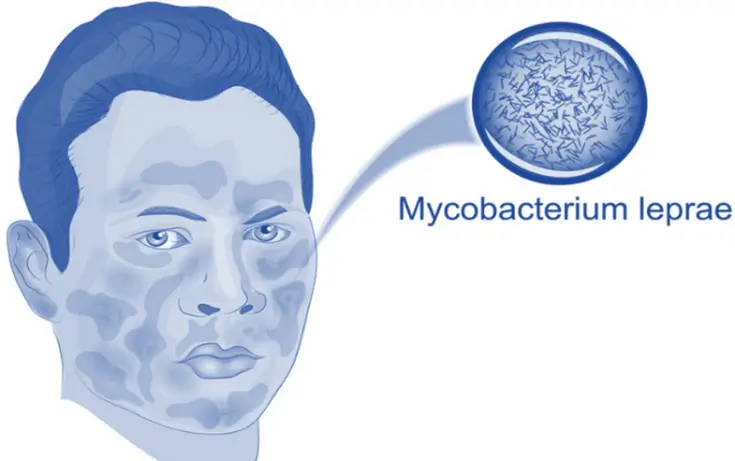
- Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae, which primarily affects the skin, peripheral nerves, respiratory system, and eyes.
- It has a long incubation period, sometimes taking years to manifest symptoms.
Signs and Symptoms
-
Early Signs:
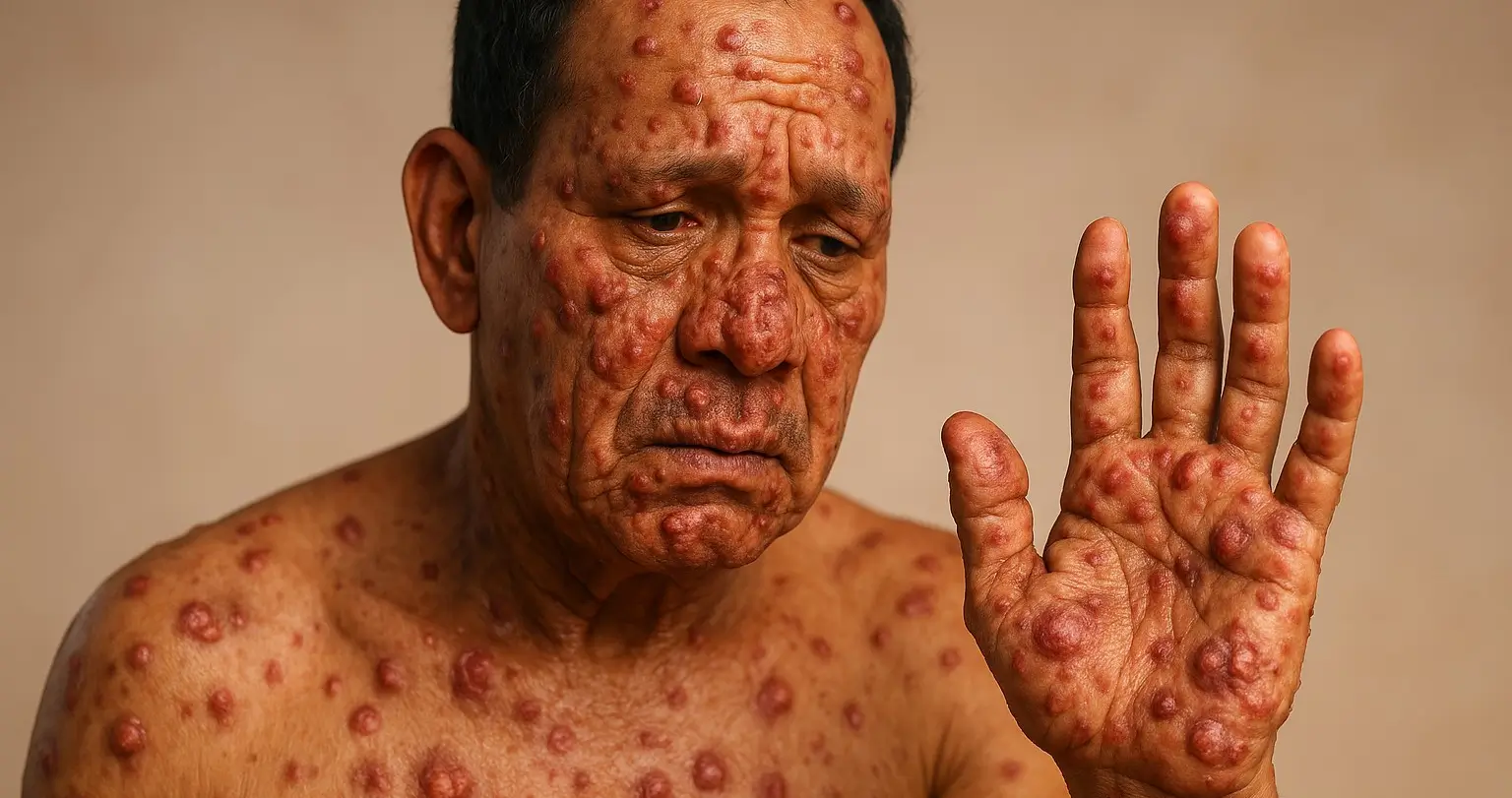
- Skin Lesions: Pale or reddish patches that are numb to touch.
- Numbness: Loss of sensation in affected areas.
- Muscle Weakness: Often in the hands and feet.
-
Progressive Symptoms:
- Thickened Skin: Nodules and thickened dermal areas.
- Eye Problems: Reduced blinking reflex, dryness, potential blindness.
- Ulcers: Chronic skin ulcers, especially on the soles of the feet.
- Deformities: Claw-like hands or drop foot due to nerve damage.
- Loss of Eyebrows and Eyelashes: Common in advanced cases.
Types of Leprosy
- Based on the Ridley-Jopling Classification:
-
Tuberculoid Leprosy (TT):
- Few skin lesions, high nerve involvement, strong immune response.
-
Borderline Tuberculoid Leprosy (BT):
- Intermediate between tuberculoid and borderline lepromatous.
-
Borderline Leprosy (BB):
- Intermediate form with more lesions and moderate immune response.
-
Borderline Lepromatous Leprosy (BL):
- Numerous lesions, weaker immune response.
-
Lepromatous Leprosy (LL):
- Many skin lesions and nodules, poor immune response, more severe.
-
Advertisements
Etiology
- Causative Agent: Mycobacterium leprae.
- Transmission: Likely through prolonged close contact with an untreated person, possibly via respiratory droplets.
Pathogenesis
- Entry: leprae enters the body, possibly through the skin or respiratory tract.
- Spread: Bacteria preferentially infect peripheral nerves, skin, upper respiratory tract, and eyes.
- Immune Response: Depending on the host’s immune response, the disease can manifest as either paucibacillary (limited) or multibacillary (widespread).
Treatment
-
Multidrug Therapy (MDT):
- Paucibacillary: Dapsone and rifampicin for 6 months.
- Multibacillary: Dapsone, rifampicin, and clofazimine for 12 months.
-
Supportive Care:
- Physical therapy, surgical interventions for deformities, and eye care.
Prevention:
- Early diagnosis and treatment to reduce transmission.
- Contact tracing and screening of household contacts.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements