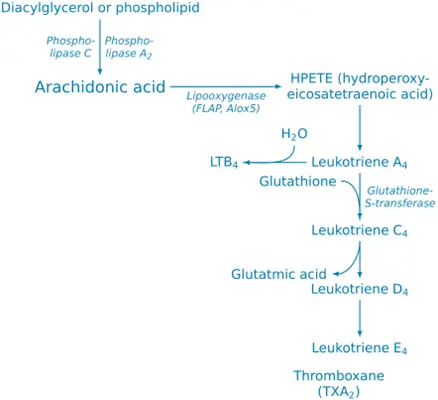
- Leukotrienes are eicosanoids derived from arachidonic acid via the lipoxygenase (LOX) pathway.
- Leukotrienes are primarily involved in immune and inflammatory responses.
- These three groups are collectively called eicosanoids, derived from arachidonic acid via the cyclooxygenase (COX) or lipoxygenase pathways.
Major Leukotrienes:
-
LTB4 (Leukotriene B4):
- Functions: Acts as a potent chemotactic agent, attracting neutrophils to sites of inflammation.
-
LTC4, LTD4, LTE4 (Cysteinyl Leukotrienes):
- Functions: Induce bronchoconstriction, increase vascular permeability, and contribute to inflammatory responses.
Advertisements
Synthesis:
- Immune Cells Activation: Upon stimulation, cells like mast cells, eosinophils, and macrophages release arachidonic acid.
- LOX Pathway: 5-LOX converts arachidonic acid into leukotriene A4 (LTA4), which is further transformed into LTB4 or conjugated with glutathione to form LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4.
Arachidonic acid → (5-lipoxygenase) → Leukotriene A4 → LTB4, LTC4, LTD4, LTE4.
Advertisements
Physiological and Pathological Roles:
- Asthma and Allergies: Cysteinyl leukotrienes mediate bronchoconstriction and increased mucus production.
- Inflammation: LTB4 recruits and activates leukocytes, amplifying the inflammatory response.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Involved in the pathogenesis of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Advertisements
Pharmacological Effects of Leukotrienes:
- Bronchoconstriction: Cause tightening of airway muscles, contributing to asthma and allergic reactions.
- Increased Vascular Permeability: Promote leakage of fluids into tissues, leading to edema.
- Chemotaxis: Attract immune cells like neutrophils to sites of inflammation.
- Mucus Secretion: Stimulate mucus production in the respiratory tract.
- Pain Sensitization: Enhance pain perception during inflammatory responses.
Drug targets:
- 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor: Zileuton (used in asthma).
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists: Montelukast, Zafirlukast (for asthma prophylaxis).
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements

