Lidocaine Hydrochloride is a class Ib anti-arrhythmic for acute ventricular arrhythmias, blocking sodium entry in heart cells.
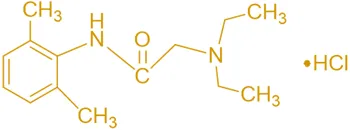
Structure of Lidocaine Hydrochloride
- Lidocaine hydrochloride is an amide-type local anesthetic with a diethylaminoethyl side chain attached to a 1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-imidazolidinone core. It exists as the hydrochloride salt to enhance solubility.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₂H₂₁N₃O · HCl
Mode of Action
- Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Blockade: Inhibits sodium influx in neurons and cardiac cells, preventing action potential initiation and propagation.
- Membrane Stabilization: Stabilizes neuronal membranes by increasing threshold for action potential generation.
- Anticonvulsant and Antiarrhythmic Effects: Reduces neuronal excitability and suppresses ventricular arrhythmias.
Advertisements
Uses
- Local Anesthesia: Provides numbing in surgical procedures, dental work, and minor skin surgeries.
- Cardiac Arrhythmias: Treats ventricular arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation.
- Epilepsy: Used intravenously as an anticonvulsant in status epilepticus.
- Pain Management: Employed in nerve blocks and epidural anesthesia.

