- Lipid metabolism involves the synthesis, transport, and breakdown of lipids in the body.
- Lipids are diverse organic compounds, including fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesterol.
- They play critical roles in cellular structure, energy storage, and signaling.
- Lipid metabolism is divided into anabolic (lipid synthesis) and catabolic (lipid breakdown) pathways.
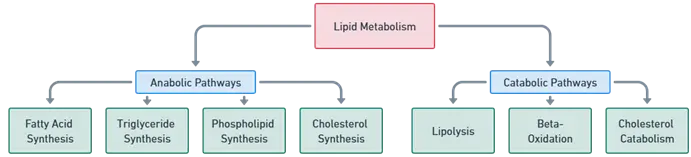
Anabolic Pathways of Lipid Metabolism
-
Fatty Acid Synthesis:
-
Triglyceride Synthesis:
- Function: Triglycerides are the primary form of energy storage in adipose tissue.
- Process: Synthesized from glycerol-3-phosphate and fatty acids through esterification.
- Location: Takes place in the endoplasmic reticulum of cells.
-
Phospholipid Synthesis:
- Function: Phospholipids are essential components of cell membranes.
- Process: Synthesized from glycerol-3-phosphate, fatty acids, and a polar head group (e.g., choline, ethanolamine, serine).
- Location: Occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum.
-
Cholesterol Synthesis:
- Function: Cholesterol is vital for cell membranes and is a precursor for steroid hormones and bile acids.
- Process: Synthesized from acetyl-CoA in a complex, multi-step process.
- Location: Primarily occurs in the liver.
- Key Enzymes: HMG-CoA reductase and squalene synthase.
Catabolic Pathways of Lipid Metabolism
-
Lipolysis:
- Process: Triglycerides stored in adipose tissue are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids by lipases, particularly hormone-sensitive lipase.
- Products: Glycerol can be converted to glucose in the liver, and fatty acids can be used for energy through beta-oxidation.
-
Beta-Oxidation:
- Process: Fatty acids are transported into mitochondria and broken down into acetyl-CoA units through a series of enzymatic reactions.
- Outcome: Acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle (TCA cycle) to generate ATP, carbon dioxide, and water.
-
Cholesterol Catabolism:
- Process: Excess cholesterol is converted to bile acids in the liver.
- Excretion: Bile acids are secreted into the small intestine and excreted in feces.
-
Regulation and Health Implications
- Regulation: Lipid metabolism is regulated by hormones such as insulin, glucagon, and adrenaline, as well as dietary factors and cellular energy status.
- Health Issues: Imbalances in lipid metabolism can lead to obesity, insulin resistance, and atherosclerosis.
-
- Understanding lipid metabolism is crucial for maintaining health and managing conditions related to lipid imbalances.