Lovastatin is a statin drug that lowers cholesterol levels by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, reducing cardiovascular risk.
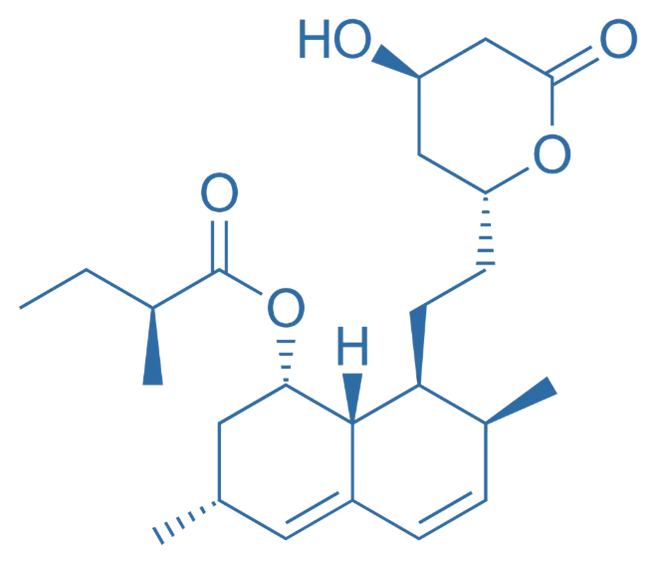
Structure of Lovastatin
- Lovastatin is a natural statin derived from Aspergillus terreus, featuring a dihydroxyheptanoic acid side chain and a lactone ring.
- Chemical Formula: C₂₅H₃₆O₅
Mode of Action
- HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibition: Blocks the enzyme hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting step in cholesterol synthesis.
- Cholesterol Synthesis Reduction: Decreases hepatic cholesterol production, leading to upregulation of LDL receptors.
- LDL-C Lowering: Enhances clearance of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) from the bloodstream.
- Plaque Stabilization: Reduces inflammation and stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques.
Uses
- Hypercholesterolemia: Lowers elevated LDL-C and total cholesterol levels.
- Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: Reduces the risk of myocardial infarction and stroke in patients with dyslipidemia.
- Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Manages inherited high cholesterol levels.

