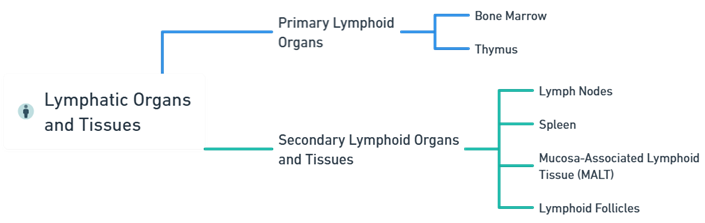
- Lymphatic Organs and Tissues: Vital for the immune system, providing environments for immune cells to develop, mature, and interact with antigens.
- Lymphatic Organs and Tissues are classified into primary lymphoid organs (where lymphocytes are generated and mature) and secondary lymphoid organs (where immune responses are initiated).
Primary Lymphoid Organs and Tissues
Bone Marrow
- Soft tissue in bone cavities, site of hematopoiesis (blood cell production).
- B cells are generated and mature here, expressing unique antigen receptors.
Thymus
- Bi-lobed organ in the upper chest, where T cells mature and differentiate.
- Immature T cells from the bone marrow undergo selection to ensure proper immune response.
Advertisements
Secondary
Lymph Nodes
- Bean-shaped structures along lymphatic vessels containing B cells, T cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells.
- Filter lymph, trap pathogens, and facilitate immune cell-antigen interactions to initiate adaptive immune responses.
Spleen
- Organ in the upper left abdomen that filters blood, removes old red blood cells, recycles iron, and hosts immune responses to bloodborne pathogens.
Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT)
- Lymphoid tissues in mucous membranes (e.g., gastrointestinal, respiratory tracts).
- Includes Peyer’s patches, tonsils, and adenoids, protecting against pathogens entering through mucosal surfaces.
Lymphoid Follicles
- Clusters of immune cells, mainly B cells, in secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes, spleen, and MALT.
- Crucial for B cell activation and antibody production.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements