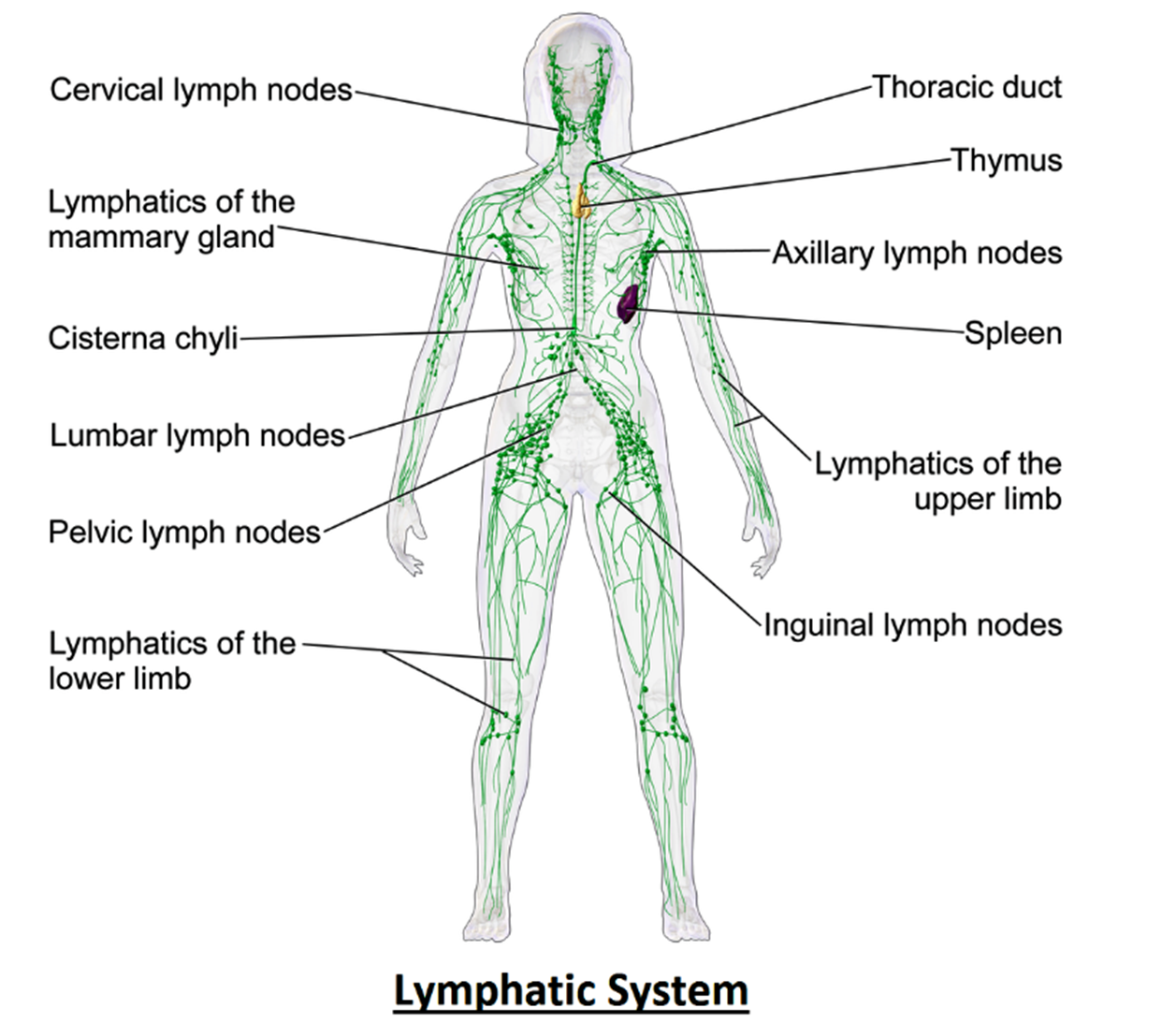
- The lymphatic system is a crucial part of the circulatory and immune systems.
- It is a network of vessels, tissues, and organs that help maintain fluid balance, remove waste products, and defend the body against infections and diseases.
Main Components of the Lymphatic System
Lymphatic Vessels
- A network of thin-walled vessels that transport lymph, a clear fluid containing excess interstitial fluid, proteins, waste, and immune cells.
- Present throughout the body (except CNS, avascular tissues, and bone marrow), they help maintain fluid balance by returning excess fluid to the bloodstream.
Advertisements
Lymph Nodes
- Small, bean-shaped structures along lymphatic vessels, rich in lymphocytes (B and T cells) and macrophages.
- Filter lymph, detect and eliminate pathogens, and serve as sites for immune cell activation and proliferation.
Lymphoid Organs
- Specialized organs involved in immune function.
- Primary: Bone marrow and thymus (where lymphocytes are generated and mature).
- Secondary: Spleen, tonsils, adenoids, Peyer’s patches (where immune cells interact with antigens and initiate immune responses).
Advertisements
Lymphocytes
- White blood cells crucial for adaptive immunity.
- B cells: Produce antibodies.
- T cells: Regulate immune responses and attack infected or abnormal cells.
Advertisements
The lymphatic system performs several essential functions, including
Fluid balance
- It helps maintain fluid balance by collecting excess interstitial fluid from tissues and returning it to the bloodstream.
Waste removal
- The lymphatic system transports waste products, cellular debris, and foreign particles away from tissues for elimination.
Immune defence
- The lymphatic system is involved in both innate and adaptive immune responses.
- Lymph nodes and other lymphoid organs filter pathogens and abnormal cells from lymph, and immune cells in these tissues help detect and eliminate threats.
Advertisements
Fat absorption
- Lymphatic vessels in the intestines, known as lacteals, absorb dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the digestive system and transport them to the bloodstream.