Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic used to reduce intracranial and intraocular pressure by drawing fluid out through the kidneys.
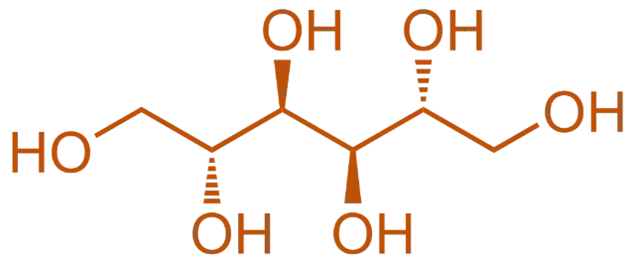
Structure of Mannitol
- Mannitol is a sugar alcohol with six hydroxyl groups, making it highly hydrophilic and osmotic.
- Chemical Formula: C₆H₁₄O₆
Advertisements
Mode of Action
- Osmotic Gradient Creation: Mannitol remains in the extracellular space, creating an osmotic gradient that pulls water out of cells and into the vascular compartment.
- Increased Urinary Output: Promotes diuresis by preventing water reabsorption in the kidneys.
- Reduction of Intracranial Pressure: Draws fluid out of brain tissue, reducing intracranial pressure.
- Reduction of Intraocular Pressure: Lowers pressure within the eye by promoting aqueous humor excretion.
Advertisements
Uses
- Intracranial Hypertension: Reduces elevated intracranial pressure in conditions like traumatic brain injury and cerebral edema.
- Acute Renal Failure: Helps restore renal function by increasing urine output and reducing edema.
- Glaucoma: Lowers intraocular pressure to prevent optic nerve damage.
- Contrast-Induced Nephropathy Prevention: Used prophylactically to protect kidneys during radiologic procedures involving contrast agents.
- Dehydration: Manages severe dehydration by promoting rapid water excretion.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements

