Meclorethamine is an alkylating anti-cancer drug that inhibits DNA replication, used in treating Hodgkin’s lymphoma and other cancers.
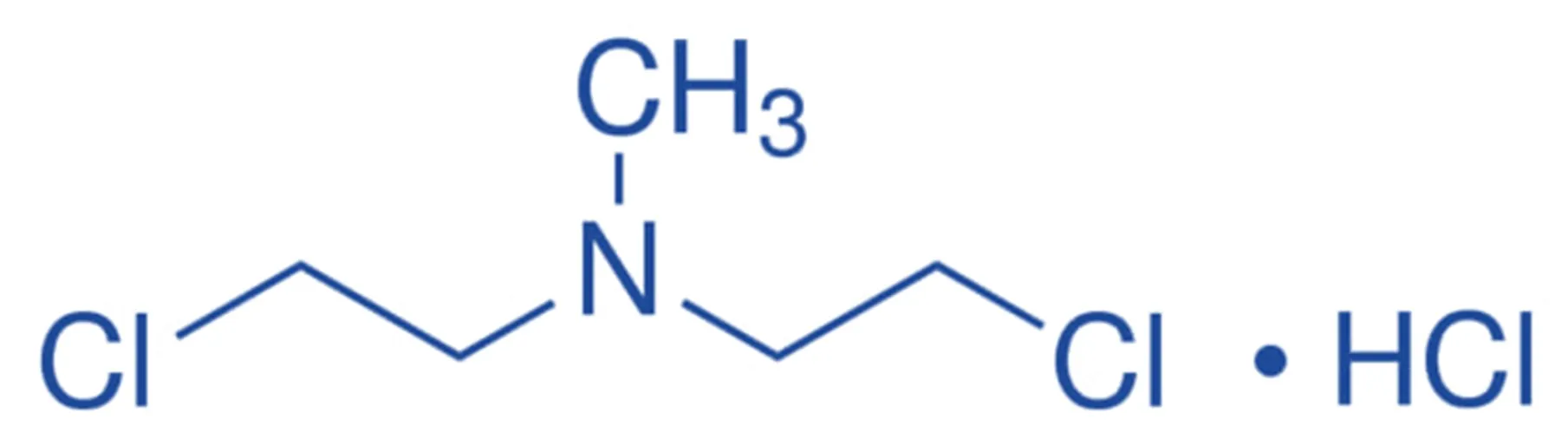
Structure of Meclorethamine
- Meclorethamine, also known as nitrogen mustard, is one of the first alkylating agents used in chemotherapy.
- Its structure comprises:
- A mustard moiety with two chloroethyl groups attached to a nitrogen atom.
- Chemical Formula: C₄H₉Cl₂N
Mode of Action
- Meclorethamine functions as an alkylating agent that:
- Crosslinks DNA: It forms covalent bonds with DNA, leading to interstrand and intrastrand crosslinks.
- Inhibits DNA Replication and Transcription: By crosslinking DNA strands, it prevents cancer cells from proliferating.
- Induces Apoptosis: The DNA damage triggers programmed cell death in rapidly dividing cells.
Advertisements
Uses
- Lymphomas: Particularly Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- Leukemias: Various forms of leukemia.
- Other Cancers: Such as multiple myeloma and certain solid tumors.
Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
- Chloroethyl Groups: Essential for alkylation; the presence and position of chloro groups influence reactivity and potency.
- Nitrogen Atom: Acts as the central point for chloroethyl attachment; its substitution pattern affects the drug’s ability to form crosslinks.
- Hydrocarbon Chain Length: Affects the spacing between alkylating sites, influencing DNA binding efficiency.
- Substituents: Electron-withdrawing or donating groups can modulate the electrophilicity of the chloroethyl groups, impacting reactivity.
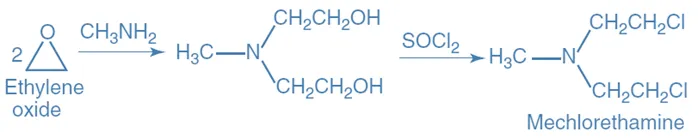
Synthesis of Meclorethamine