- Melatonin is a natural hormone produced by the pineal gland in the brain that helps regulate the body’s sleep-wake cycle, also known as the circadian rhythm.
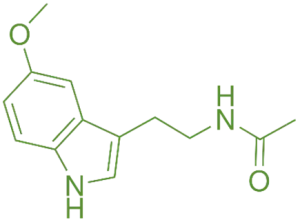
Synthesis of Melatonin:
-
Step 1: Conversion to N-acetylserotonin:
-
- Enzyme: Arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (AANAT).
- Process: Serotonin is acetylated to form N-acetylserotonin.
- Mechanism: AANAT transfers an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to serotonin, producing N-acetylserotonin.
-
Step 2: Conversion to Melatonin:
-
- Enzyme: Hydroxyindole-O-methyltransferase (HIOMT).
- Process: N-acetylserotonin is methylated to form Melat.
- Mechanism: HIOMT transfers a methyl group from S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) to N-acetylserotonin, producing melatonin’s.
Significance:
- Sleep-Wake Cycle: Regulates the sleep-wake cycle by signaling to the body when it’s time to sleep, aligning the internal clock with external light-dark cycles.
- Antioxidant Properties: It has antioxidant effects, protecting cells from oxidative stress.
- Immune Function: It supports the immune system and has anti-inflammatory properties.
Clinical Relevance of Melatonin:
- Sleep Disorders: It supplements are used to treat conditions like insomnia, jet lag, and circadian rhythm disorders.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos