Metformin is a biguanide antidiabetic drug that lowers blood sugar by reducing hepatic glucose production and improving insulin sensitivity.
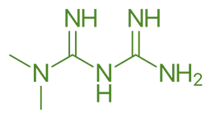
Structure of Metformin
- Metformin is a biguanide derivative with two guanidine groups attached to a dimethylamine backbone.
- Chemical Formula: C₄H₁₁N₅
Mode of Action
- AMP-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) Activation: Enhances insulin sensitivity and reduces hepatic gluconeogenesis.
- Intestinal Glucose Uptake Inhibition: Decreases glucose absorption from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Decreased Lipolysis: Reduces free fatty acid levels, improving insulin sensitivity.
Uses
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: First-line therapy for improving glycemic control.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Enhances insulin sensitivity and regulates menstrual cycles.
- Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes: In individuals with impaired glucose tolerance.

