- Methadone Hydrochloride manages opioid dependence and chronic pain with long-lasting effects.
- It acts as a μ-opioid receptor agonist with NMDA antagonism for analgesia.
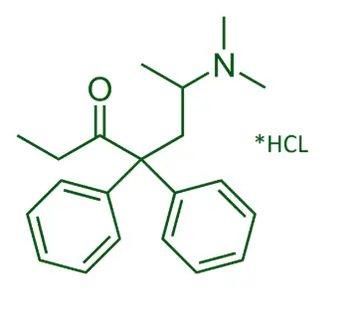
Chemical Formula:
- C₂₁H₂₇NO·HCl
Mechanism of Action:
- Full μ-opioid receptor agonist
- Also, NMDA antagonist and inhibits monoamine reuptake
- Very long half-life (15–60 hrs) → minimal withdrawal fluctuations
Advertisements
Uses of Methadone Hydrochloride:
- Opioid maintenance therapy (OMT) in addiction treatment
- Chronic severe pain
Side Effects of Methadone Hydrochloride:
- Respiratory depression (long-lasting)
- QT prolongation
- Sedation
- Constipation
SAR of Methadone:
-
Diphenylpropylamine structure:
- Central for opioid activity.
-
Tertiary amine:
- Protonated form interacts with μ-opioid receptors.
-
Two phenyl rings:
- Important for receptor binding; contribute to potency.
-
Ketone group:
- Increases polarity and contributes to partial NMDA antagonism.
-
Chiral center:
- (R)-methadone is the active isomer at opioid receptors.
-
Extended duration of action:
- Due to slow metabolism and high lipophilicity.
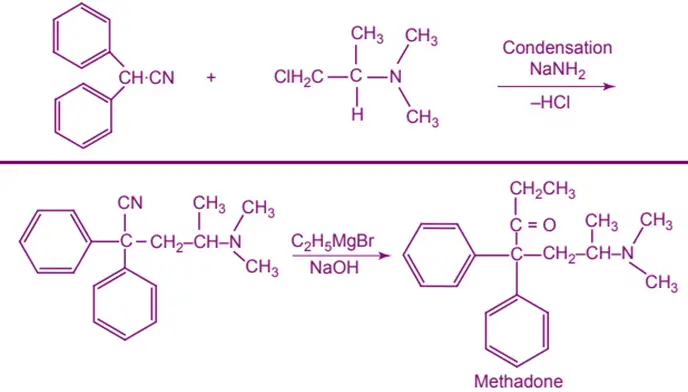
Synthesis of Methadone:
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements

