Methimazole is an antithyroid drug used to manage hyperthyroidism by inhibiting thyroid hormone production.
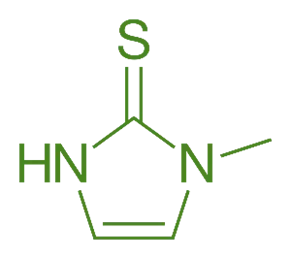
Structure of Methimazole
- Methimazole is an antithyroid drug with a thiourea structure, featuring a methyl group attached to the nitrogen of the thiourea moiety.
- Chemical Formula: C₄H₈N₂S
Mode of Action
- Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Inhibition: Similar to propylthiouracil, methimazole inhibits thyroid peroxidase, blocking iodination of tyrosine residues and coupling of iodotyrosines to form T3 and T4.
- Iodine Organification Inhibition: Prevents the incorporation of iodine into thyroid hormones.
- Peripheral Conversion Inhibition: Minimally inhibits the peripheral conversion of T4 to T3.
Uses
- Hyperthyroidism: Treats Graves’ disease, toxic multinodular goiter, and toxic adenoma by reducing thyroid hormone synthesis.
- Thyroid Storm: Less commonly used than propylthiouracil but still effective in managing acute hyperthyroid crises.
- Thyroid Cancer Preparation: Lowers thyroid hormone levels prior to radioactive iodine therapy or surgical intervention.
- Thyroiditis: Manages hyperthyroidism associated with thyroiditis.
Side Effects of Methimazole
- Agranulocytosis: Risk of severe white blood cell count reduction.
- Hepatotoxicity: Potential liver damage.
- Rash and Allergic Reactions: Includes skin rashes, itching, and other hypersensitivity responses.
- Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- Joint Pain: May cause arthralgia and myalgia.

