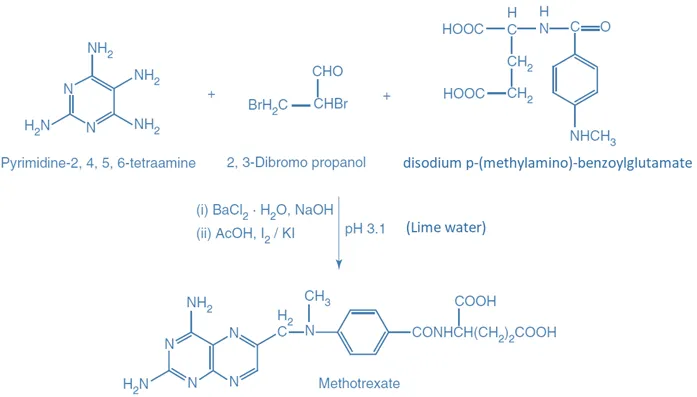
Methotrexate is an anti-neoplastic antimetabolite used to treat leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer by inhibiting DNA synthesis.
Structure of Methotrexate
- It is a folate analog with the following structural features:
- Pteridine Ring: Core structure similar to folic acid.
- Glutamate Residues: Multiple glutamate moieties attached to the pteridine ring.
- Chemical Formula: C₂⁰H₂⁷N₇O₇
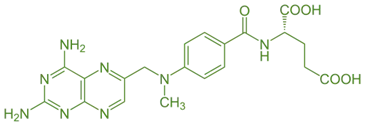
Mode of Action
- Methotrexate acts as an antimetabolite and antifolate by:
- Inhibition of Dihydrofolate Reductase (DHFR): Prevents the conversion of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate, essential for DNA synthesis.
- Inhibition of Thymidylate Synthase: Reduces dTMP synthesis, hindering DNA replication.
- Induction of Apoptosis: Causes cytotoxicity in rapidly dividing cells.
Advertisements
Uses of Methotrexate
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): As part of multi-agent chemotherapy.
- Breast Cancer: In certain treatment protocols.
- Ovarian Cancer: Alongside other chemotherapeutic agents.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: As a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD).
- Psoriasis: In severe cases unresponsive to other treatments.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: To terminate non-viable pregnancies.
Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)