Methyldopate Hydrochloride is a centrally acting antihypertensive used to lower blood pressure by reducing sympathetic nerve signals.
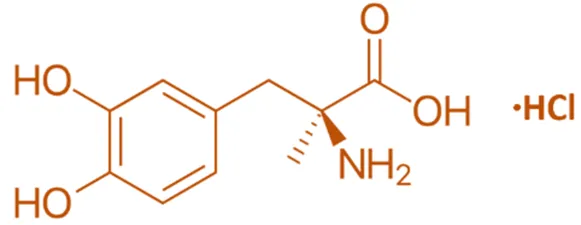
Structure of Methyldopate Hydrochloride
- It is an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist with a phenethylamine backbone substituted with a hydroxyl group and a chlorine atom.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₁H₁₆ClN₂O·HCl
Advertisements
Mode of Action
- Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonism: Activates presynaptic alpha-2 receptors in the central nervous system.
- Sympathetic Inhibition: Reduces sympathetic outflow, decreasing peripheral vascular resistance and lowering blood pressure.
- Sedative Effects: Promotes central nervous system depression, contributing to its antihypertensive effects.
Advertisements
Uses
- Hypertension: Primarily used in the management of resistant hypertension.
- ADHD: Employed off-label for its sedative and concentration-enhancing effects.
- Anxiety Disorders: Utilized for its calming effects.
- Opioid Withdrawal: Assists in managing symptoms by reducing sympathetic hyperactivity.
Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
- Phenethylamine Backbone: Essential for binding to alpha-2 adrenergic receptors.
- Hydroxyl Group: Increases hydrophilicity and enhances receptor affinity.
- Chlorine Substituent: Enhances lipophilicity, improving blood-brain barrier penetration and potency.
- Substituents on the Aromatic Ring: Modifications can affect receptor selectivity and binding affinity.
Advertisements
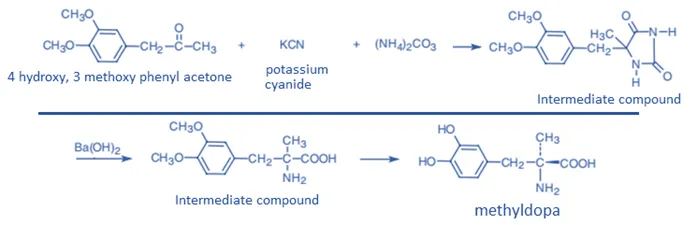
Synthesis of Methyldopate Hydrochloride