- Metoprolol is a selective beta-1 adrenergic receptor blocker (β1-blocker) used primarily to manage cardiovascular conditions.
- It reduces the effects of adrenaline on the heart, leading to decreased heart rate, cardiac output, and blood pressure.
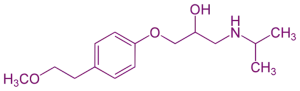
Chemical Structure & Formula:
- Comprises an aromatic ring joined to an oxypropanolamine chain and is typically used as a racemic mixture (with the (S)-enantiomer being more active).
- Approximate Formula: C₁₅H₂₅NO₃

Mechanism of Action:
- Selectively blocks β₁ receptors in the heart, reducing heart rate, contractility, and myocardial oxygen demand.
Side Effects of Metoprolol:
- Bradycardia and hypotension
- Fatigue and dizziness
- Occasional gastrointestinal disturbances
Advertisements
Clinical Uses of Metoprolol:
- Widely used for hypertension, angina, arrhythmias, and in post–myocardial infarction management.