- Mixing powders is a critical process in preparing pharmaceutical products like tablets, capsules, and bulk powders.
- The goal is to create a homogenous blend of active ingredients and excipients for consistent dosing.
- Powder mixing can be done through manual or mechanical
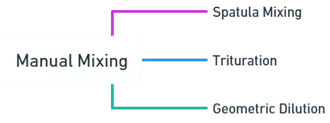
1. Manual Mixing
- Manual mixing uses simple tools like spatulas, mortars, and pestles to blend powders. Common techniques include:
-
Spatula Mixing:
- Powders are blended on a flat surface using a spatula by cutting, folding, and pressing until uniformly mixed.
-
Trituration:
- A mortar and pestle are used to grind and mix powders in a circular motion for a uniform blend.
-
Geometric Dilution:
- Used when a potent ingredient is mixed with a larger amount of diluent.
- Small portions of each are mixed, doubling the quantity with more diluent until the desired blend is achieved.
Advertisements
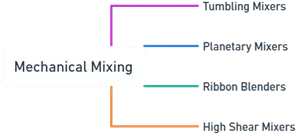
2. Mechanical Mixing
- Mechanical mixing uses equipment for more efficient and consistent blending. Common methods include:
-
Tumbling Mixers:
- Powders are placed in a container that rotates or tumbles.
- Examples: V-blenders, double cone blenders.
-
Planetary Mixers:
- A rotating impeller mixes powders while revolving around the container’s axis, ensuring thorough blending.
-
Ribbon Blenders:
- Consist of a U-shaped trough with a helical ribbon that moves and mixes powders, ideal for large volumes.
-
High Shear Mixers:
- Use high-speed impellers to create intense shear forces, breaking up and mixing powders, commonly used for suspensions and granulations

