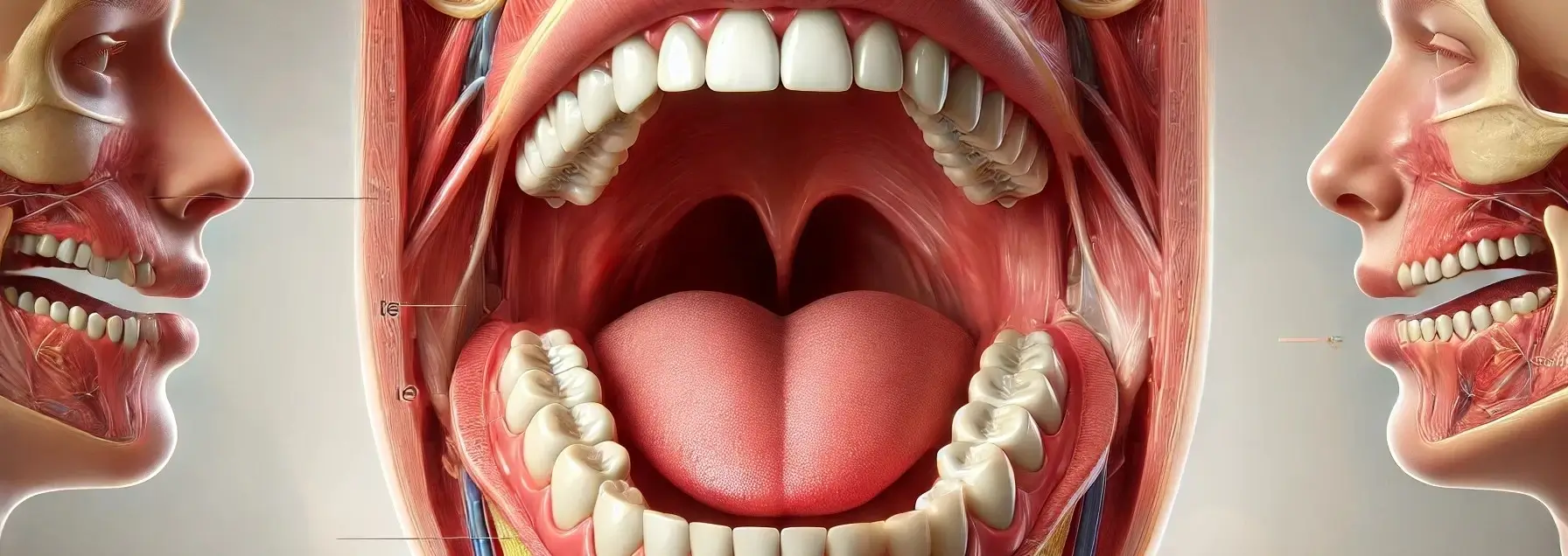
- The oral cavity, or mouth, marks the entry point of the digestive system, equipped with specialized structures for the initial processing of food.
- Here, food encounters teeth and salivary glands, which work in concert to reduce food to a consistency suitable for digestion and absorption further down the GI tract.
Teeth:
- The Tools for Mechanical Digestion
- Teeth are hard, calcified structures embedded in the dental arches of the mouth.
- They are instrumental in the mechanical breakdown of food, a process known as mastication or chewing.
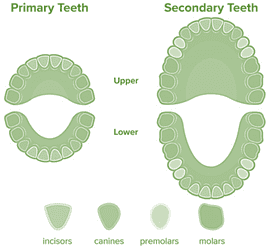
- Humans have two sets of teeth over their lifetime: deciduous (baby) teeth and permanent (adult) teeth.
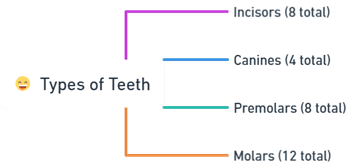
Types of Teeth in Adults:
Advertisements
- Incisors (8 total): These are the front teeth, sharp and chiseled-shaped, designed for biting and cutting food.
- Canines (4 total): Located next to the incisors, canines are pointed and used for tearing and ripping food.
- Premolars (8 total): Situated next to the canines, premolars have a broader surface for crushing and grinding food.
- Molars (12 total): These are the back teeth, equipped with large, flat surfaces ideal for grinding and pulverizing food.
Tongue:
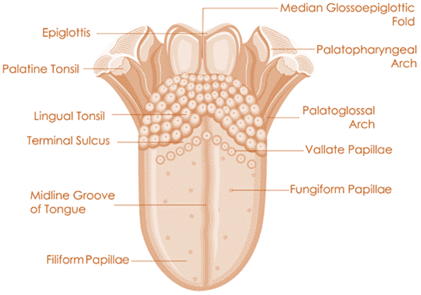
- The Versatile Muscular Organ
- The tongue, a muscular organ found on the floor of the mouth, plays multiple roles in the digestive and sensory systems.
Functions of the Tongue:
- Tasting: The surface of the tongue is studded with taste buds that allow us to discern five basic tastes: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami.
- Manipulation of Food: It assists in moving food around the mouth to ensure even mixing with saliva and effective chewing.
- Formation of the Bolus: The tongue aids in shaping chewed food into a bolus, a compact mass ready for swallowing.
- Swallowing: It then propels the bolus towards the pharynx, triggering the swallowing process.
Salivary Glands:
- Facilitators of Chemical Digestion
- Role in Digestion:
- These glands secrete saliva, which moistens food for easier chewing and swallowing.
- Saliva contains enzymes, such as amylase, which initiate the breakdown of carbohydrates into simpler sugars right in the mouth.
Advertisements