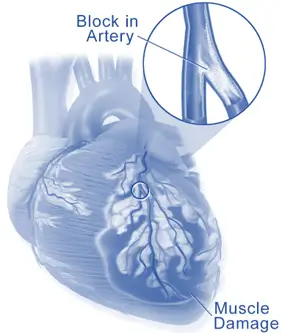
- Myocardial infarction (MI), or heart attack, occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked for a long enough time to cause damage or death of the heart muscle.
Types
-
ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI):
- Severity: Severe type where a major coronary artery is completely blocked.
- ECG Changes: ST-segment elevation on the electrocardiogram.
-
Non-ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI):
- Severity: Less severe; artery is partially blocked.
- ECG Changes: No ST-segment elevation but may show other signs of heart damage.
Etiology
- Atherosclerosis: Rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque and subsequent blood clot formation.
- Coronary Artery Spasm: Severe spasm reducing blood flow to the heart.
Pathogenesis of Myocardial Infarction
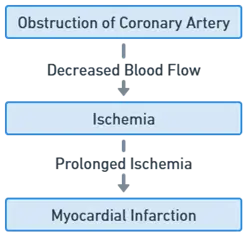
- Plaque Rupture: Atherosclerotic plaque in a coronary artery ruptures.
- Thrombus Formation: A blood clot forms at the rupture site, completely blocking blood flow.
- Ischemia and Necrosis: Lack of oxygenated blood leads to death of heart muscle tissue (infarction).
Advertisements
Signs and Symptoms
- Chest Pain: Intense, persistent pain or pressure.
- Radiating Pain: Pain may extend to arms, neck, jaw, or back.
- Shortness of Breath: Due to impaired oxygen delivery.
- Other Symptoms: Sweating, nausea, vomiting, light-headedness, fatigue.
Management and Treatment
-
Emergency Treatment
- Immediate medical attention.
- Oxygen therapy.
- Pain relief (e.g., morphine).
- Nitroglycerin administration.
-
Medications
- Thrombolytics: Dissolve blood clots.
- Antiplatelet Agents: Aspirin, clopidogrel.
- Beta-blockers: Reduce heart workload.
- ACE Inhibitors: Lower blood pressure.
- Statins: Lower cholesterol levels.
-
Medical Procedures
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): Angioplasty and stenting to open blocked arteries.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): Surgery to bypass blocked arteries.