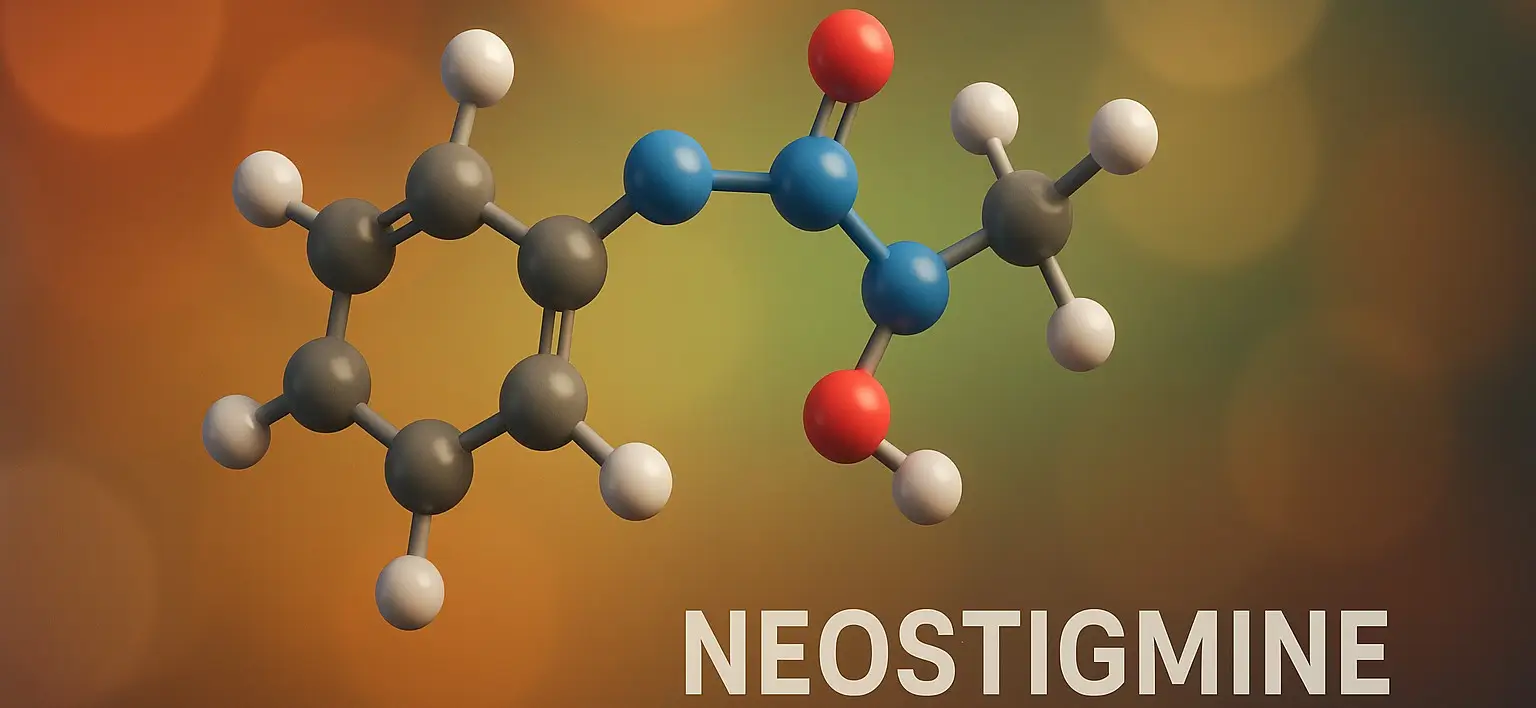
- Neostigmine is a synthetic quaternary ammonium compound that acts as a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor.
- It inhibits the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, thereby increasing the concentration of acetylcholine at neuromuscular junctions and cholinergic synapses.
Chemical Formula:
- C₁₂H₁₉N₂O₂⁺

Mechanism of Action:
- Reversible AChE inhibitor.
- Also has some direct nicotinic agonist activity at NMJ.
Uses of Neostigmine:
- Myasthenia gravis
- Reversal of non-depolarizing neuromuscular blockers (e.g. tubocurarine)
- Postoperative ileus and urinary retention
Side Effects of Neostigmine:
- Bradycardia
- Salivation
- Muscle cramps
- Diarrhea
- Hypotension
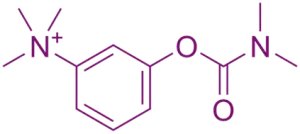
SAR of Neostigmine:
-
Carbamate group:
- Forms a reversible covalent bond with AChE → temporary inhibition.
-
Quaternary ammonium group:
- Mimics choline portion of acetylcholine.
- Prevents CNS penetration; acts peripherally.
-
Phenolic ring:
- Enhances binding to acetylcholinesterase via interactions at peripheral sites.
-
Steric hindrance:
- Affects rate of carbamoylation and decarbamoylation of the enzyme.
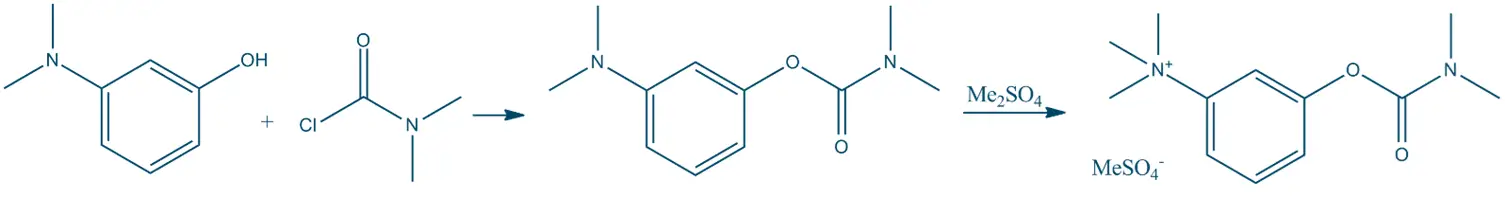
General Synthesis:

Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos