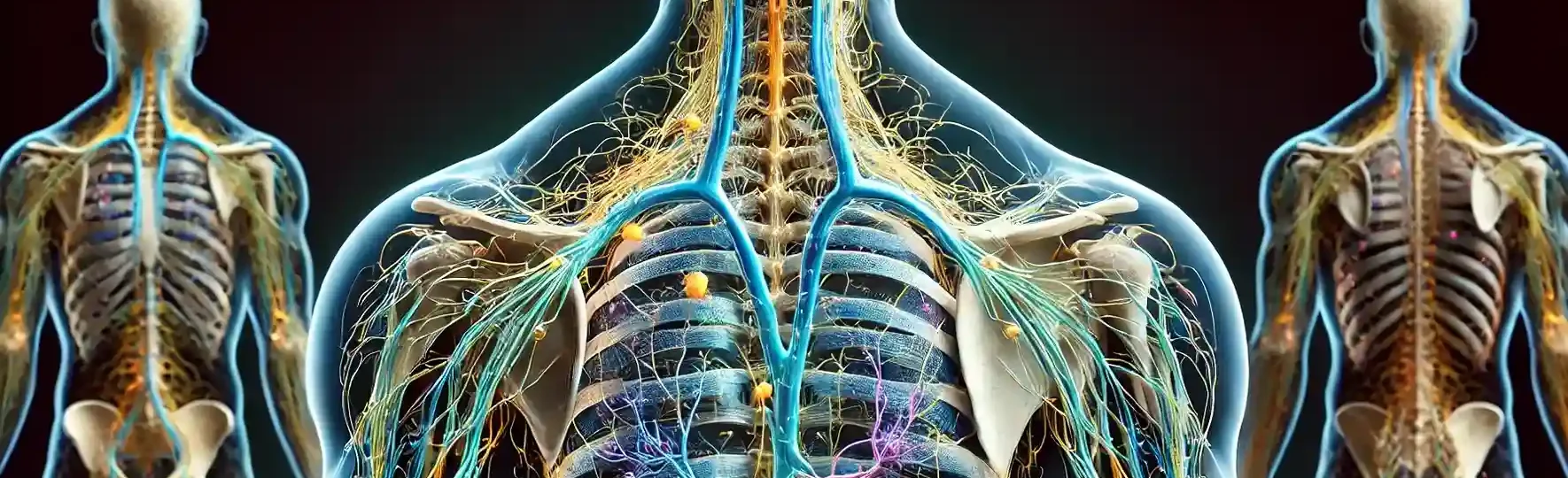
Nerve Plexuses
- In the context of Nerve Plexuses & Reflex Actions, a nerve plexus is a complex network of intersecting nerves that redistributes fibers from multiple spinal nerves, enabling shared sensory and motor functions.
- The four major nerve plexuses are:
1.Cervical Plexus (C1-C4):
- Located in the neck, supplies muscles and skin of the neck and head.
- Includes the phrenic nerve, crucial for diaphragm function and breathing.
2. Brachial Plexus (C5-T1):
- Located in the shoulder; innervates the upper limbs (shoulder, arm, forearm, hand).
- Major nerves: median, ulnar, radial, axillary, and musculocutaneous
3. Lumbar Plexus (L1-L4):
- Located in the lower back; supplies the lower abdomen, groin, and anterior thigh.
- Major nerves: femoral and obturator
Advertisements
4. Sacral Plexus (L4-S4):
- Located in the pelvis; innervates the buttocks, posterior thigh, leg, and foot.
- Major nerve: sciatic nerve, the largest in the body.
Reflex Actions
- A reflex action is a fast, involuntary response to stimuli that bypasses the brain and follows a reflex arc. It involves:
- Receptor: Detects stimulus (pain, pressure, etc.).
- Sensory Neuron: Carries the signal to the spinal cord.
- Integration Center: Processes information in the spinal cord.
- Motor Neuron: Sends the response to the effector.
- Effector: Carries out the response (muscle contraction or gland secretion).