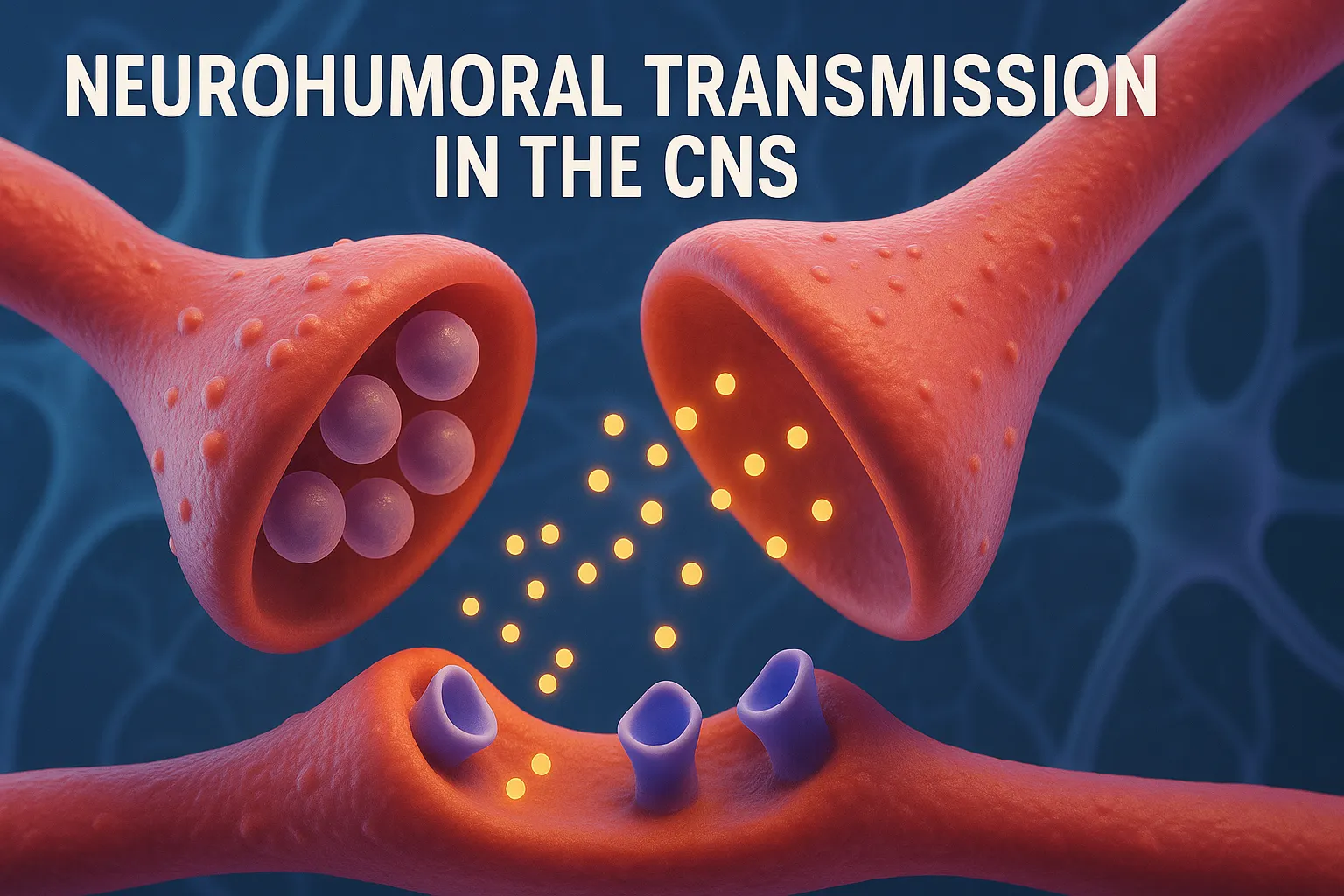
Neurohumoral Transmission in the CNS
- Neurohumoral transmission refers to the chemical communication between neurons via neurotransmitters across synapses.
- Neurohumoral transmission in the CNS involves chemical messengers like neurotransmitters regulating brain signaling.
Steps in CNS Neurotransmission:
- Synthesis of neurotransmitter in the presynaptic neuron.
- Storage in synaptic vesicles.
- Release into synaptic cleft via exocytosis (triggered by Ca²⁺ influx).
- Binding to specific postsynaptic receptors.
- Termination by:
Types of Neurotransmitters
- Neurotransmitters can be broadly categorized into:
- Excitatory (e.g., Glutamate)
- Inhibitory (e.g., GABA, Glycine)
- Modulatory (e.g., dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine)
- Each neurotransmitter has specific receptors and associated second messenger pathways which determine the cellular response.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos