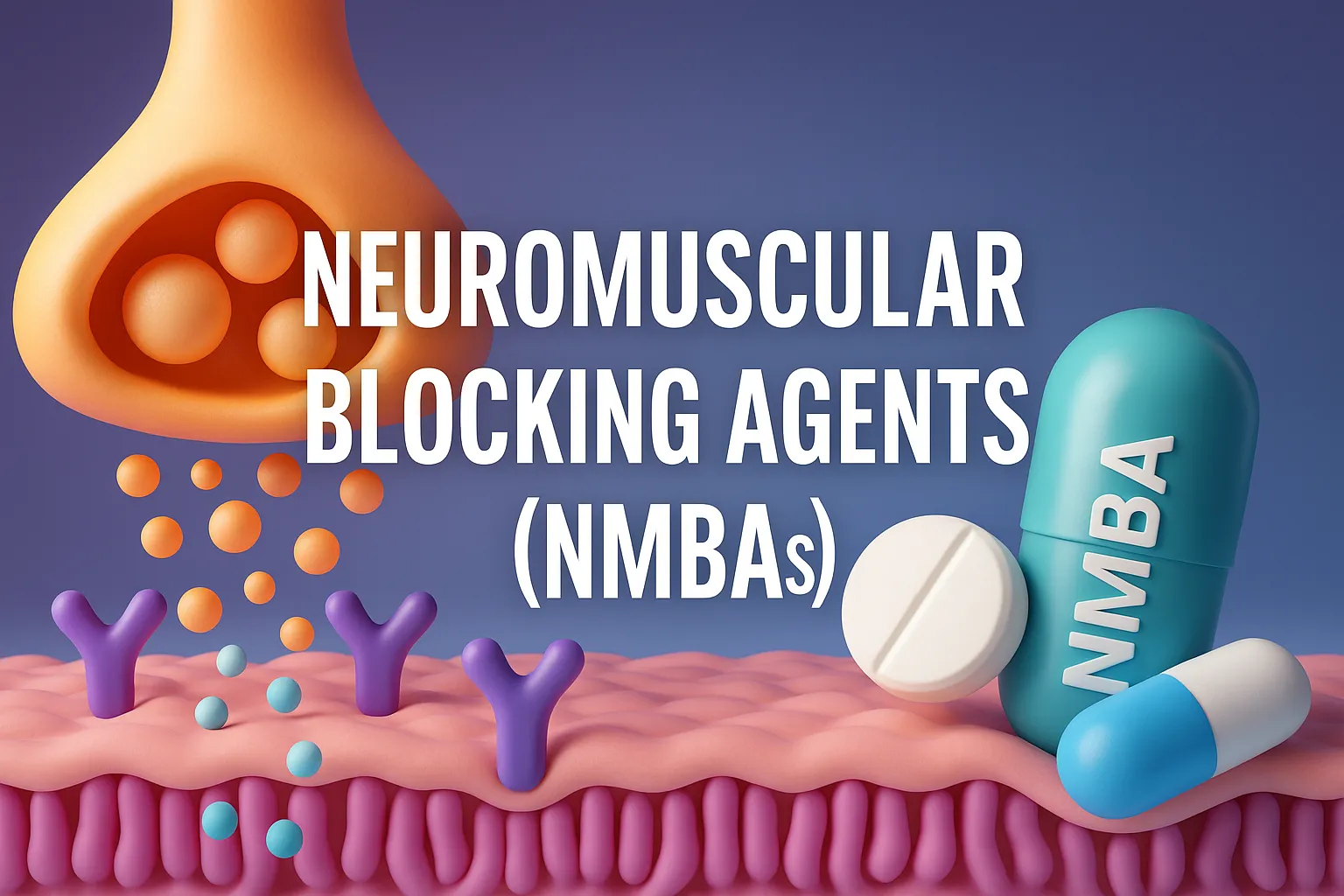
Neuromuscular blocking agents cause muscle relaxation by blocking transmission at neuromuscular junctions.
Neuromuscular Blocking Agents (NMBAs)
- These are drugs that interfere with transmission of nerve impulses at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ).
- They cause paralysis of skeletal muscles by blocking the action of acetylcholine (ACh), the neurotransmitter that mediates nerve impulses to muscles.
- They do not affect consciousness or pain perception, which is why general anesthesia or sedation is needed concurrently.
Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ):
- The neuromuscular junction is the synapse between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle fiber.
- It is where the nerve signal is transmitted to the muscle, causing contraction.
Key Steps:
- Nerve impulse reaches the end of the motor neuron.
- Acetylcholine (ACh) is released into the synaptic cleft.
- ACh binds to nicotinic receptors on the muscle membrane (motor endplate).
- This causes depolarization of the muscle membrane → muscle contraction.
- ACh is broken down by acetylcholinesterase (AChE) to stop the signal.