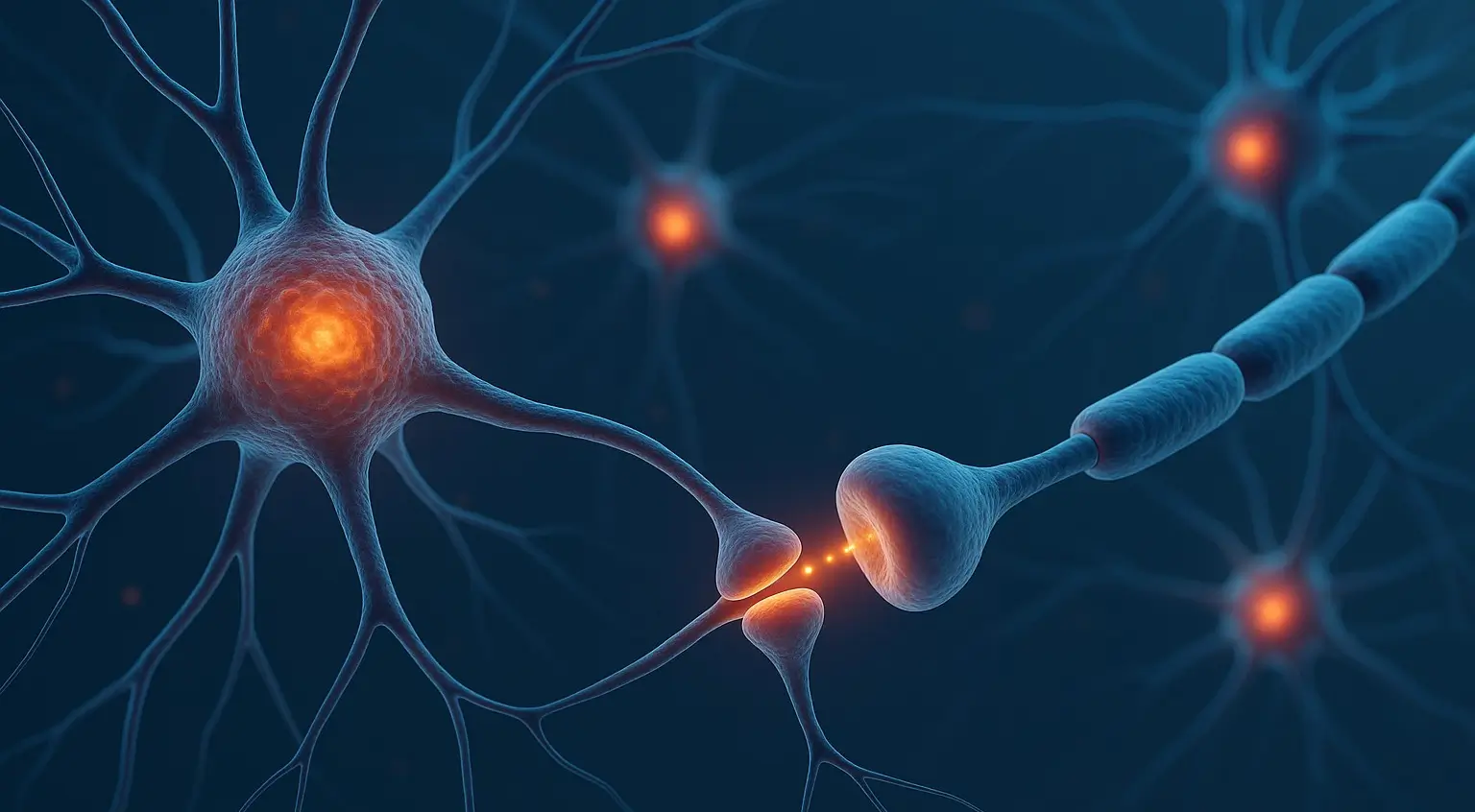
Neurons and Synapses Definition
- neurons and synapses, representing the fundamental unit of neural communication where electrical or chemical signals are transmitted from one neuron to another.
- It emphasizes the inseparable relationship between the nerve cell (neuron) and its connection point (synapse) in processing and transmitting information within the nervous system.
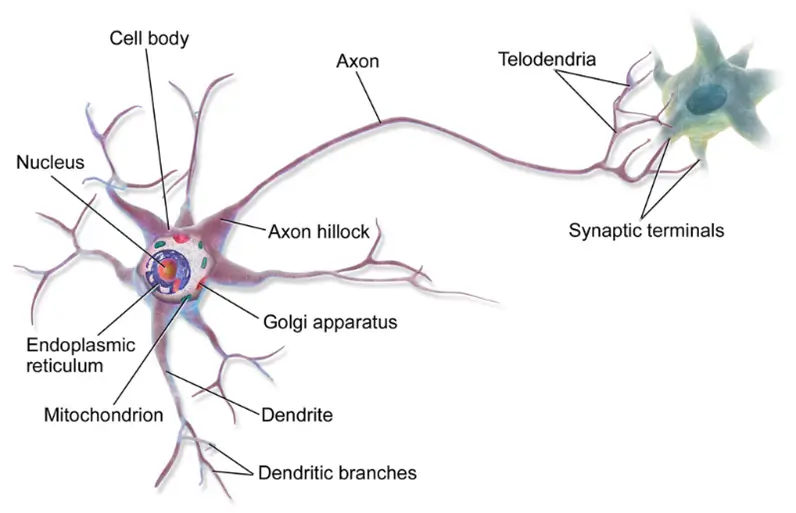
Neurons
- Neurons are the fundamental units of the brain and nervous system. They are specialized cells that transmit information through electrical and chemical signals.
- A neuron consists of:
- Dendrites (receive signals)
- Cell body (Soma) (processes signals)
- Axon (sends signals)
- Axon terminals (release neurotransmitters)
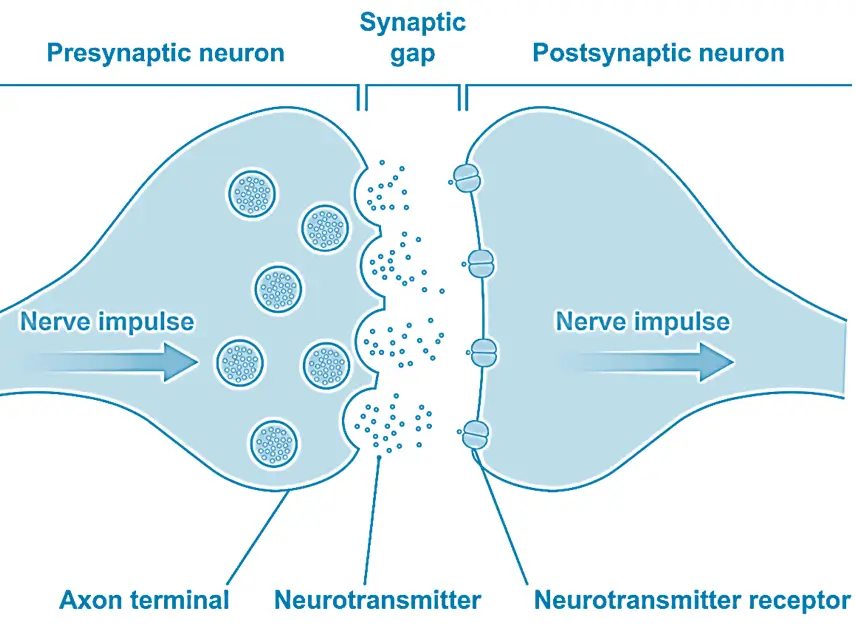
Synapse
- A synapse is the junction between two neurons where communication occurs.
- It consists of:
- Presynaptic neuron – Sends the signal.
- Synaptic cleft – The gap between neurons.
- Postsynaptic neuron – Receives the signal.
Types
- Chemical Synapses – Use neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin.
- Electrical Synapses – Direct, faster connections via gap junctions.
How They Work Together
- A neuron receives a signal.
- The signal travels down the axon.
- Neurotransmitters are released into the synapse.
- The next neuron receives and processes the signal.
Functions of the Nervous System
- The nervous system performs three primary functions:
-
Sensory Function
- Sensory nerves gather information from both inside the body and the external environment.
- This information is then transmitted to the central nervous system.
-
Integrative Function
- The brain processes sensory information, leading to sensations, thought processes, and memory formation.
-
Motor Function
- Motor nerves carry information from the central nervous system to muscles and glands, enabling them to function.
-
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos