Oestradiol is a potent estrogen that regulates menstrual cycles, fertility, and secondary sexual traits.
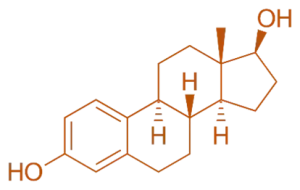
Structure of Oestradiol
- Oestradiol is the most potent endogenous estrogen, featuring a cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene structure with two hydroxyl groups at the 3 and 17 positions.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₈H₂₄O₂
Mode of Action
- Estrogen Receptor Activation: Binds to estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ), regulating gene expression involved in reproductive and non-reproductive systems.
- Reproductive Functions: Stimulates the development of female secondary sexual characteristics, regulates the menstrual cycle, and prepares the endometrium for implantation.
- Bone Health: Promotes bone formation and inhibits bone resorption, preventing osteoporosis.
- Cardiovascular Effects: Improves lipid profiles by increasing HDL-C and decreasing LDL-C, and promotes vasodilation.
- Neuroprotective Roles: Influences cognitive function and mood regulation.
Advertisements
Uses
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Alleviates menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and osteoporosis prevention.
- Contraception: Used in combination with progestins in oral contraceptives.
- Gender-Affirming Therapy: Administered to transgender women to develop female secondary sexual characteristics.
- Breast Cancer Treatment: Utilized in hormone-sensitive breast cancers to modulate estrogen effects.
- Premature Ovarian Insufficiency: Supports estrogen levels in women with ovarian failure.