Oestrone is a natural estrogen important for female reproductive health and postmenopausal hormone balance.
Structure of Oestrone
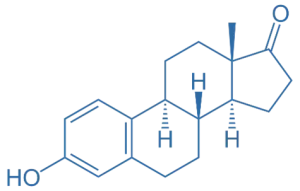
- Oestrone is one of the three primary endogenous estrogens, characterized by a cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene structure with a ketone group at the 17 position and a hydroxyl group at the 3 position.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₈H₂₄O₂
Mode of Action
- Estrogen Receptor Activation: Binds to estrogen receptors, regulating gene expression related to reproductive and various systemic functions.
- Reproductive Functions: Involved in the menstrual cycle, ovulation, and maintenance of the endometrium.
- Bone Health: Supports bone density by promoting bone formation and inhibiting resorption.
- Cardiovascular Effects: Enhances lipid profiles and promotes vasodilation, contributing to cardiovascular health.
- Metabolic Regulation: Influences carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Advertisements
Uses
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Sometimes used in HRT regimens to alleviate menopausal symptoms.
- Contraception: Employed in combination with progestins in certain oral contraceptives.
- Hormonal Balance: Used in managing hormone-related disorders such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Breast Cancer Research: Studied for its role in hormone-sensitive breast cancers.
- Osteoporosis Prevention: Assists in maintaining bone density in postmenopausal women.

