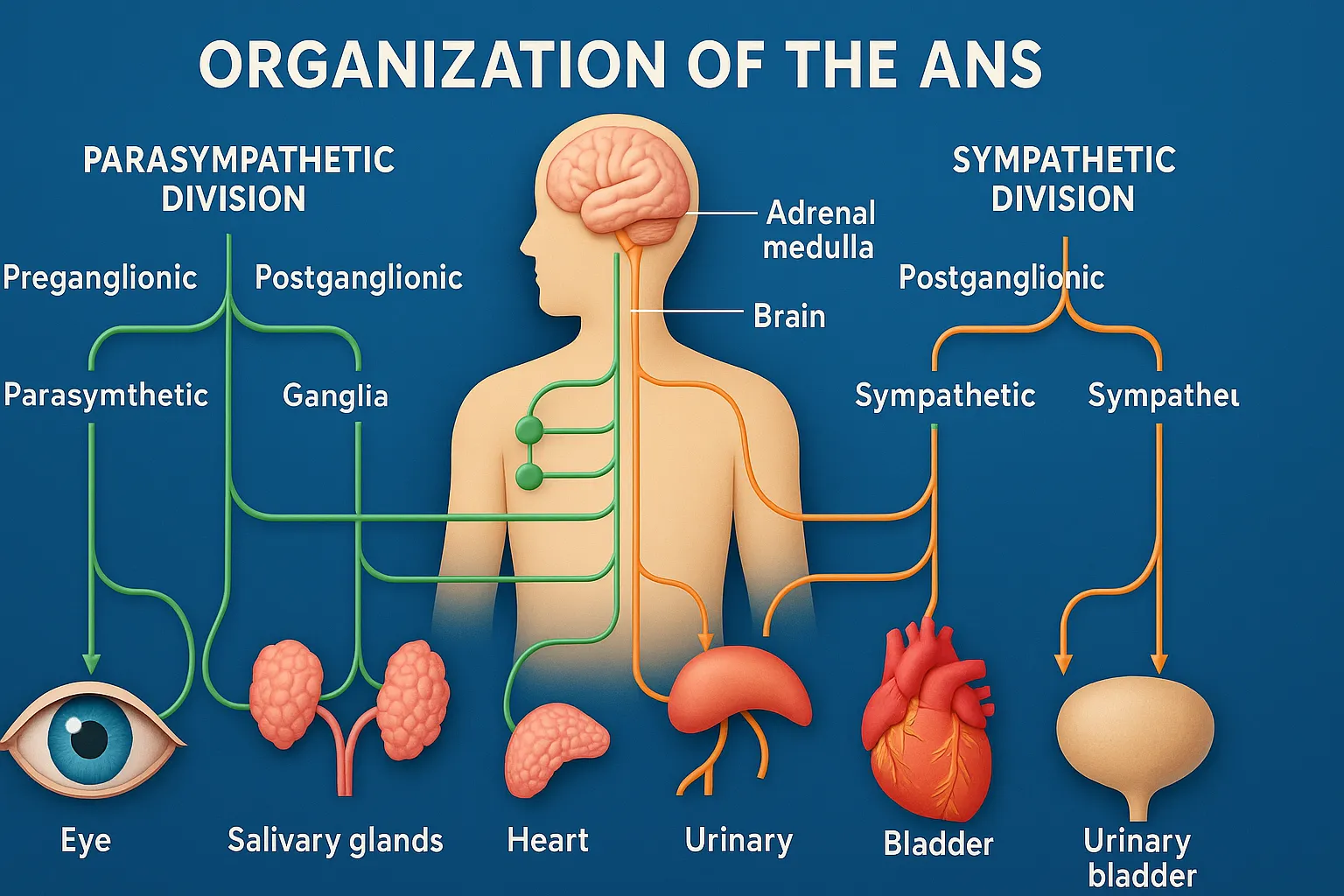
Organization of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) includes sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions controlling involuntary functions.
What is the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)?
- The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) is a part of the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) that controls involuntary body functions—those that happen without conscious thought.
- It regulates: Heart rate, Breathing rate, Digestion, Pupillary response, Urination, sexual arousal, and more
- It ensures that the internal environment of the body remains stable, a state called homeostasis.
Organization of the ANS
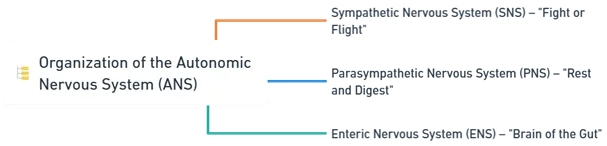
The ANS is divided into three main components:
-
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS) – “Fight or Flight”
- Origin: Thoracolumbar region (T1–L2) of the spinal cord
- Function: Prepares the body for stressful or emergency situations
- Key Effects:
- Increases heart rate and blood pressure
- Dilates pupils
- Inhibits digestion
- Dilates bronchioles (for more oxygen)
- Mobilizes energy (glucose release)
-
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS) – “Rest and Digest”
- Origin: Craniosacral region (brainstem and sacral spinal cord)
- Function: Promotes relaxation and conserves energy
- Key Effects:
- Slows heart rate
- Stimulates digestion
- Constricts pupils
- Promotes urination and defecation
- Encourages sexual arousal
-
Enteric Nervous System (ENS) – “Brain of the Gut”
- Location: Embedded in the lining of the gastrointestinal tract
- Function: Controls gastrointestinal functions independently but is influenced by both sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
- Key Effects:
- Regulates enzyme secretion
- Controls peristalsis (movement of food)
- Manages blood flow in the gut
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic – Key Differences
| Feature | Sympathetic | Parasympathetic |
| Function | Fight or flight | Rest and digest |
| Origin | Thoracolumbar | Craniosacral |
| Ganglia Location | Close to spinal cord | Near or within target organ |
| Neurotransmitter | NE (mostly) | ACh |
| Effect on Heart | Increases rate | Decreases rate |
| Effect on Digestion | Inhibits | Stimulates |