- The pancreas is a vital organ that lies in the abdomen, behind the stomach and in close proximity to the duodenum.
- It plays a crucial role in both the digestive system and the endocrine system, making it unique in its functions and importance to overall health.
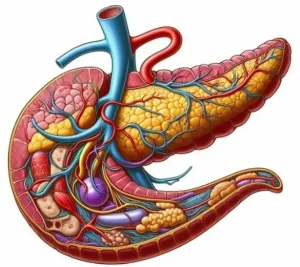
Structure of Pancreas
-
Location and Appearance:
- Elongated organ located behind the stomach, stretching across the back of the abdomen.
-
Parts of the Pancreas:
- Head: Widest part, nestled in the curve of the duodenum.
- Body: Extends toward the left side of the body.
- Tail: Narrow part, extending to the spleen.
-
Tissue Composition:
Function of Pancreas
-
Exocrine Function:
- Produces digestive enzymes (lipase, protease, amylase) that break down fats, proteins, and carbohydrates in the small intestine.
-
Endocrine Function:
Advertisements
Disorders of Pancreas
-
Diabetes Mellitus:
- Type 1: Autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing beta cells, leading to insulin deficiency.
- Type 2: Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency.
-
Pancreatitis:
- Inflammation of the pancreas:
- Acute: Caused by gallstones or alcohol, leading to sudden abdominal pain.
- Chronic: Long-term inflammation causing permanent damage.
- Inflammation of the pancreas:
-
Pancreatic Cancer:
-
Cystic Fibrosis:
- Genetic disorder affecting the exocrine pancreas, leading to blocked ducts, poor enzyme secretion, malnutrition, and poor growth.
-
Insulinoma:
- Rare tumor causing excessive insulin production, leading to hypoglycemia.
Treatment of Pancreas
-
Diabetes:
- Managed through blood glucose monitoring, diet and lifestyle changes, insulin injections, or oral medications.
-
Acute Pancreatitis:
- Requires hospitalization for pain management, hydration, and sometimes surgery to remove blockages.
-
Chronic Pancreatitis:
- Managed with pain relief, pancreatic enzyme supplements, and dietary adjustments.
-
Pancreatic Cancer:
- Treated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy depending on the stage and location of the cancer.
-
Cystic Fibrosis:
- Focuses on symptom management, including pancreatic enzyme supplements to aid digestion and prevent complications.