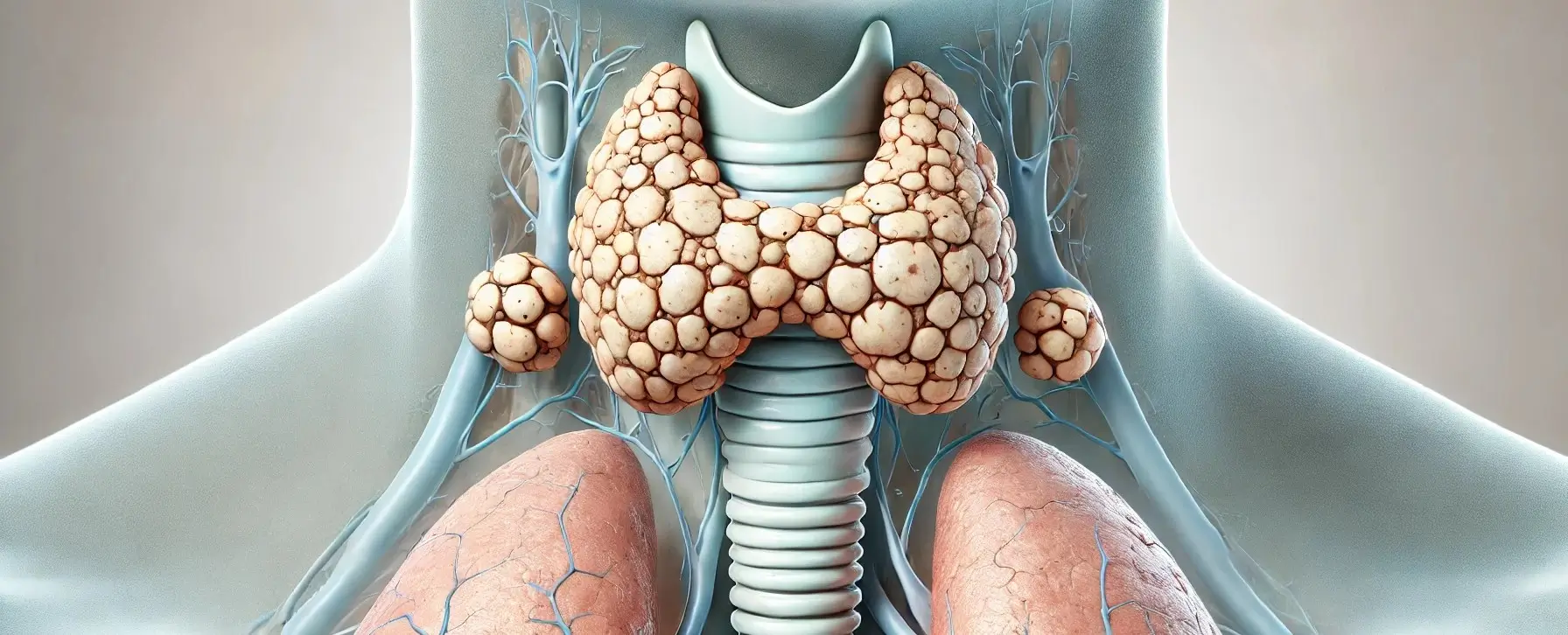
- The parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck that play a crucial role in calcium homeostasis, which is essential for various bodily functions including bone health, muscle function, and nerve signaling.
Advertisements
- Humans typically have four parathyroid glands, though the number can vary, located on the back of the thyroid gland in the neck.
Structure of Parathyroid glands
-
Location and Number:
- Usually four glands (two on each side), positioned behind the thyroid gland, though this can vary.
-
Size and Shape:
- Each gland is small, about the size of a grain of rice (3-4 mm), with a reddish-brown color.
Advertisements
Function of Parathyroid glands
- The parathyroid glands regulate calcium and phosphate levels by secreting parathyroid hormone (PTH).
- PTH increases calcium levels in the blood by:
- Stimulating calcium release from bones.
- Increasing calcium absorption in the intestines (via vitamin D activation).
- Increasing calcium reabsorption in the kidneys.
- PTH also reduces phosphate reabsorption in the kidneys, increasing phosphate excretion.
- PTH increases calcium levels in the blood by:
Disorders of the Parathyroid Glands
-
Hyperparathyroidism:
- Overproduction of PTH, causing high calcium levels (hypercalcemia).
- Often caused by a benign tumor (adenoma).
- Symptoms include osteoporosis, kidney stones, fatigue, and depression.
-
Hypoparathyroidism:
- Underproduction of PTH, leading to low calcium levels (hypocalcemia).
- Causes include surgery, autoimmune disease, or genetic factors.
- Symptoms include muscle cramps, tingling, and in severe cases, seizures.
-
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism:
- Occurs in response to low calcium levels, often due to chronic kidney disease or vitamin D deficiency.
- Prolonged condition can lead to bone disease.
Advertisements
Treatment of Parathyroid glands
- Treatment for parathyroid disorders depends on the type, cause, and severity of the condition. It may include:
- Surgery: Often recommended for primary hyperparathyroidism, to remove the overactive gland(s).
- Medication: Drugs may be used to manage symptoms or the underlying cause, such as vitamin D analogs, calcium supplements, or drugs that mimic calcium to inhibit PTH secretion in cases of hypoparathyroidism.
- Monitoring: In cases where immediate treatment isn’t necessary, regular monitoring of blood calcium levels and bone density may be advised.
- Correctly diagnosing and managing parathyroid disorders is crucial for maintaining calcium balance and preventing complications associated with abnormal calcium levels.