- Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting movement.
- It is caused by the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra, a part of the brain that controls movement.
Causes of Parkinson’s Disease
- Genetic Factors: Mutations in specific genes (e.g., LRRK2, PARK2).
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to toxins like pesticides and heavy metals.
- Age: Incidence increases with age.
- Gender: More common in men than in women.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
-
Motor Symptoms:
- Tremor: Shaking, often starting in one hand.
- Bradykinesia: Slowness of movement.
- Rigidity: Stiffness in limbs and trunk.
- Postural Instability: Impaired balance and coordination.
-
Non-Motor Symptoms:
- Cognitive impairment and dementia.
- Mood disorders: Depression and anxiety.
- Sleep disturbances: Insomnia, REM sleep behavior disorder.
- Autonomic dysfunction: Constipation, orthostatic hypotension, and urinary problems.
Diagnosis
- Clinical Evaluation: Based on medical history and neurological examination.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or DaTscan (dopamine transporter scan) to support the diagnosis.
- Response to Medication: Improvement of symptoms with dopaminergic medications supports the diagnosis.
Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disease
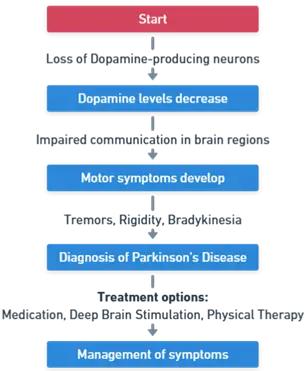
- Dopamine Deficiency: Degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of the brain.
- Lewy Bodies: Abnormal aggregates of the protein alpha-synuclein inside neurons.
- Basal Ganglia Dysfunction: Impaired regulation of motor activity leading to symptoms like bradykinesia, tremors, and rigidity.
Treatment
-
Medications:
- Levodopa: The most effective treatment, often combined with carbidopa.
- Dopamine Agonists: Mimic dopamine effects (e.g., pramipexole, ropinirole).
- MAO-B Inhibitors: Prevent breakdown of brain dopamine (e.g., selegiline, rasagiline).
- COMT Inhibitors: Prolong the effect of levodopa (e.g., entacapone).
-
Surgical Treatment:
- Deep brain stimulation (DBS) for patients with advanced symptoms not controlled by medication.
-
Physical Therapy:
- To improve mobility, balance, and flexibility.
-
Occupational Therapy:
- To assist with daily living activities.
-
Speech Therapy:
- To address speech and swallowing difficulties.

