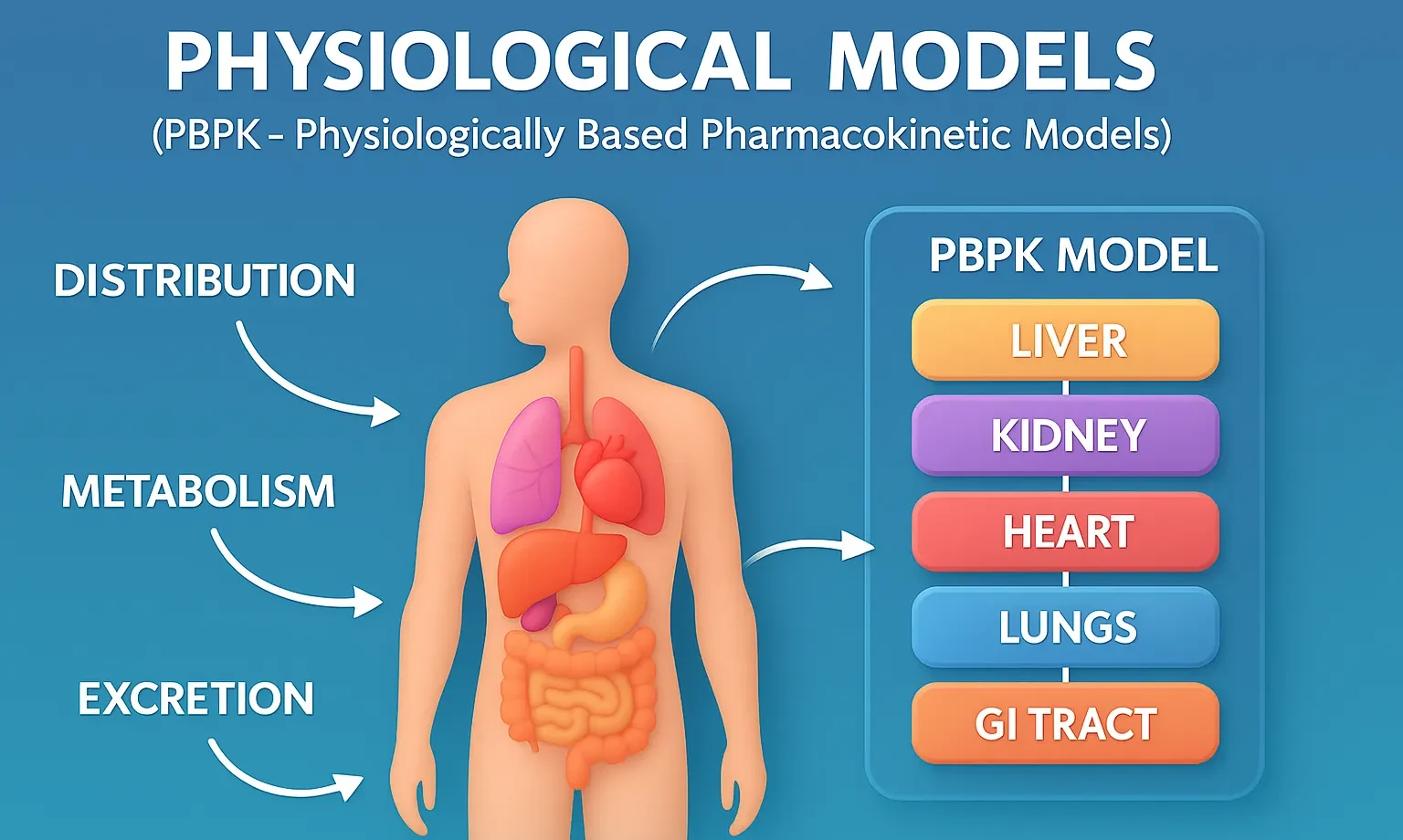
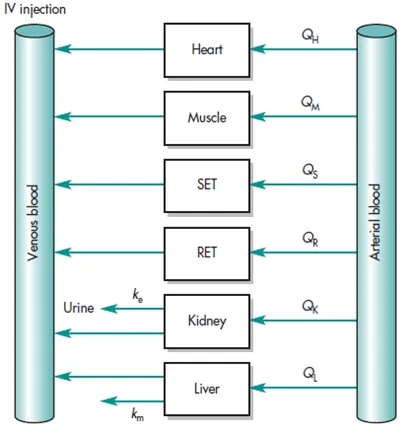
- Physiological Models (PBPK Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Models) predict drug ADME using organ physiology and blood flow data.
Physiological Models (PBPK – Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Models)
- Physiological models, or PBPK models, are the most detailed pharmacokinetic models as they incorporate actual physiological and anatomical data.
Key Features of PBPK Models:
- Based on real organ and tissue compartments (liver, kidney, brain, etc.).
- Uses blood flow rates, tissue volumes, and enzyme kinetics to predict drug behavior.
- Requires extensive physiological and biochemical data for accurate predictions.
- Simulations can be performed for different populations (children, elderly, diseased states).

Types of PBPK Models
-
Blood Flow-Limited Model
- Drug distribution depends on blood flow rate and concentration gradient between blood and tissues.
- Used for drugs with high affinity for highly perfused organs (liver, kidney, brain).
- Helps predict tissue drug concentrations and optimize dosing.
-
Membrane Permeation-Limited Model
- Drug distribution depends on membrane permeability (e.g., blood-brain barrier).
- Used for low-permeability drugs or those requiring active transport.
- Helps in designing prodrugs or nanocarriers for better absorption.
Advertisements
Applications of PBPK Models:
- Drug development and regulatory approval (FDA, EMA use PBPK for drug evaluation).
- Predicting drug-drug interactions (DDIs).
- Personalized medicine (dosing adjustments for individuals).
Advantages of PBPK Models:
- Provides the most realistic prediction of drug kinetics.
- Can be used to extrapolate data between species (e.g., from animals to humans).
- Allows prediction of organ-specific drug concentrations.
Disadvantages of PBPK Models:
- Highly complex and requires extensive data.
- Computationally intensive.
- Not always practical for routine clinical use.