Piperocaine is an ester-type local anesthetic used for infiltration and surface anesthesia by blocking nerve conduction.
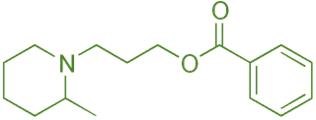
Structure of Piperocaine
- It is a synthetic local anesthetic with a piperidine ring attached to a benzamide core, enhancing its anesthetic potency and duration.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₀H₂₁N₃O
Mode of Action
- Sodium Channel Inhibition: Blocks voltage-gated sodium channels, preventing nerve impulse propagation.
- Enhanced Potency: More potent than benzocaine due to structural modifications.
Uses
- Dental Anesthesia: Employed in dental procedures for effective local numbing.
- Ophthalmic Procedures: Used in eye surgeries for corneal anesthesia.
- Minor Surgical Procedures: Applied in small-scale surgical interventions requiring local anesthesia.
Side Effects of Piperocaine
- Central Nervous System Effects: Dizziness, tremors, and in severe cases, seizures.
- Cardiovascular Toxicity: Hypotension and arrhythmias with high doses.

