Preparation of Insulin
Preparation of insulin involves extraction or recombinant DNA technology to produce purified hormone for diabetes treatment.
-
Formation of Preproinsulin:
- Insulin synthesis begins with preproinsulin (110 amino acids), synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
-
Conversion to Proinsulin:
- Preproinsulin is processed in the Golgi apparatus to form proinsulin, an inactive precursor.
-
Folding and Bond Formation:
- Proinsulin folds to form three disulfide bonds, linking the A-chain and B-chain.
-
Packaging into Vesicles:
- Folded proinsulin is packaged into secretory vesicles for further processing.
-
Cleavage by Enzymes:
- Enzymes (Proprotein Convertase 1/3 and Proprotein Convertase 2) cleave the C-peptide from proinsulin.
-
Final Processing:
- Carboxypeptidase E removes terminal amino acids, yielding active insulin.
-
Active Insulin:
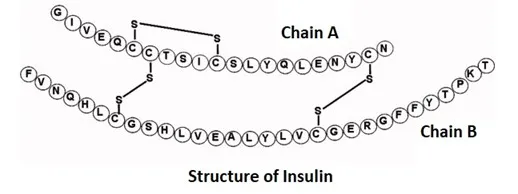
- Active insulin consists of:
- Chain A: 21 amino acids.
- Chain B: 30 amino acids.
- Chains are connected by two disulfide bonds.
- Active insulin consists of:
-
Secretion:
- Active insulin is secreted into the bloodstream to regulate blood sugar and metabolic processes.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos