Prilocaine is an amide local anesthetic commonly used in dental and infiltration anesthesia with lower toxicity risk.
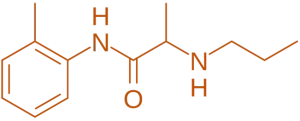
Structure of Prilocaine
- Prilocaine is an amide-type local anesthetic with an isopropyl group attached to the diethylaminoethyl side chain, providing effective anesthetic properties with reduced toxicity.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₂H₂₈N₂O
Mode of Action
- Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Blockade: Inhibits sodium influx, preventing nerve impulse conduction.
- Membrane Stabilization: Enhances neuronal membrane stability, reducing excitability.
Uses
- Local Anesthesia: Employed in dental procedures, minor surgeries, and cosmetic applications.
- Topical Preparations: Applied to skin and mucous membranes for numbing before minor interventions.
- Infiltration Anesthesia: Injected to provide localized numbness during medical procedures.
Side Effects of Prilocaine
- Methemoglobinemia: Risk of oxidizing hemoglobin to methemoglobin, reducing oxygen-carrying capacity.
- Local Irritation: Redness, swelling, or discomfort at the application site.
- Systemic Toxicity: CNS symptoms and cardiovascular disturbances in high doses.

