Promethazine Hydrochloride is a tricyclic H₁-antihistamine with sedative, antiemetic, and anticholinergic properties used in allergy and nausea treatment.
Structure of Promethazine Hydrochloride
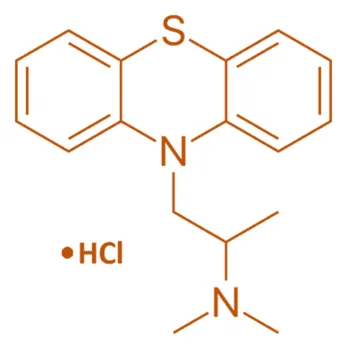
- Promethazine possesses a tricyclic structure with two benzene rings fused to a central carbon and connected to a dimethylaminoethyl side chain.
- The hydrochloride salt enhances solubility.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₇H₂₈N₂S·HCl
Mode of Action
- Acts as a potent H₁-receptor antagonist with strong anticholinergic and sedative effects.
- It also exhibits antiemetic and analgesic properties.
Uses of Promethazine Hydrochloride
- Allergic Reactions: Effective in treating symptoms like itching, sneezing, and runny nose.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Used as an antiemetic for motion sickness and post-operative nausea.
- Sedation: Utilized as a sedative and sleep aid.
- Cold Symptoms: Helps alleviate nasal congestion and other related discomforts.
Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
- Phenothiazine Core: Essential for H₁ antagonism and contributes to the drug’s lipophilicity, enhancing blood-brain barrier penetration.
- Dimethylamino Group: Critical for binding to H₁ receptors through hydrogen bonding.
- Tricyclic Structure: Provides rigidity and the necessary spatial orientation for effective receptor interaction.
- Substituents: Modifications on the benzene rings can alter potency and selectivity.
- Sulfoxide Group: Contributes to metabolic stability and activity.
Synthesis
- Promethazine can be synthesized through the reaction of chlorodiphenylmethane with piperazine, followed by methylation.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos

