Propylthiouracil is an antithyroid drug used to treat hyperthyroidism by blocking thyroid hormone synthesis.
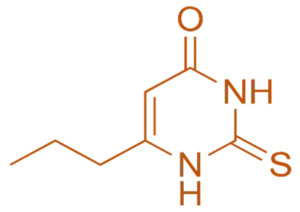
Structure of Propylthiouracil
- Propylthiouracil is an antithyroid drug with a thiouracil structure, featuring a propyl side chain attached to the uracil ring.
- Chemical Formula: C₅H₉N₃O₂S
Mode of Action
- Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Inhibition: Blocks the enzyme thyroid peroxidase, preventing the iodination of tyrosine residues and coupling of iodotyrosines to form T3 and T4.
- Iodine Organification Inhibition: Disrupts the incorporation of iodine into thyroid hormones.
- Peripheral Conversion Inhibition: Reduces peripheral conversion of T4 to the more active T3 form.
Uses
- Hyperthyroidism: Treats Graves’ disease and toxic multinodular goiter by reducing thyroid hormone production.
- Thyroid Storm: Emergency treatment of life-threatening hyperthyroidism with severe systemic effects.
- Preparation for Thyroid Surgery/Radiation: Lowers thyroid hormone levels prior to radioactive iodine therapy or surgical intervention.
- Thyroid Cancer: Used in some cases to manage thyroid hormone levels during treatment.
Side Effects of Propylthiouracil
- Agranulocytosis: Severe decrease in white blood cells, increasing infection risk.
- Hepatotoxicity: Liver damage and dysfunction.
- Rash and Allergic Reactions: Skin rashes, itching, and other hypersensitivity responses.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Gastrointestinal disturbances are common.
- Joint Pain: Arthralgia and myalgia may occur.

