- Prostaglandins act as autacoids, having diverse roles in inflammation, vascular function, and other processes.
- These three groups are collectively called eicosanoids, derived from arachidonic acid via the cyclooxygenase (COX) or lipoxygenase pathways.
- Prostaglandins are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds derived from arachidonic acid via the cyclooxygenase (COX) pathway.
Synthesis:
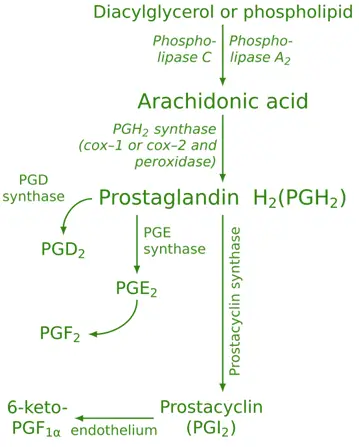
- Arachidonic Acid Release: Phospholipase A2 releases arachidonic acid from membrane phospholipids.
- COX Pathway: Cyclooxygenase enzymes (COX-1 and COX-2) convert arachidonic acid into prostaglandin H2 (PGH2).
- Further Conversion: PGH2 is a precursor for various prostaglandins (e.g., PGE2, PGI2) and thromboxanes.
Advertisements
Arachidonic acid → (COX enzyme) → prostaglandin intermediates → PGD2, PGE2, PGF2α, PGI2 (prostacyclin).
Advertisements
Major Prostaglandins:
-
PGE2 (Prostaglandin E2):
- Functions: Mediates inflammation, induces fever, modulates gastric mucosal protection, and regulates reproductive processes.
-
PGI2 (Prostacyclin):
- Functions: Inhibits platelet aggregation, induces vasodilation, protects the endothelium.
-
PGD2 (Prostaglandin D2):
- Functions: Involved in allergic responses and sleep regulation.
-
PGF2α (Prostaglandin F2α):
- Functions: Stimulates uterine contractions, involved in the menstrual cycle.
Pharmacological Effects:
- Inflammation Modulation: Promote vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, and sensitization of pain receptors, contributing to inflammation and pain.
- Gastroprotective Actions: Maintain gastric mucosal integrity by stimulating mucus and bicarbonate secretion.
- Renal Function: Regulate blood flow in the kidneys and influence sodium excretion.
- Platelet Function: Some PGs inhibit platelet aggregation, balancing thromboxane effects.
- Vascular Tone: Control vasodilation and vasoconstriction, impacting blood pressure.
- Reproductive System: Induce uterine contractions during labor and regulate menstrual cycles.
Advertisements
Examples of Prostaglandins:
- PGE₂: Mediates fever, pain, and inflammation; protects gastric lining.
- PGI₂ (Prostacyclin): Inhibits platelet aggregation and causes vasodilation.