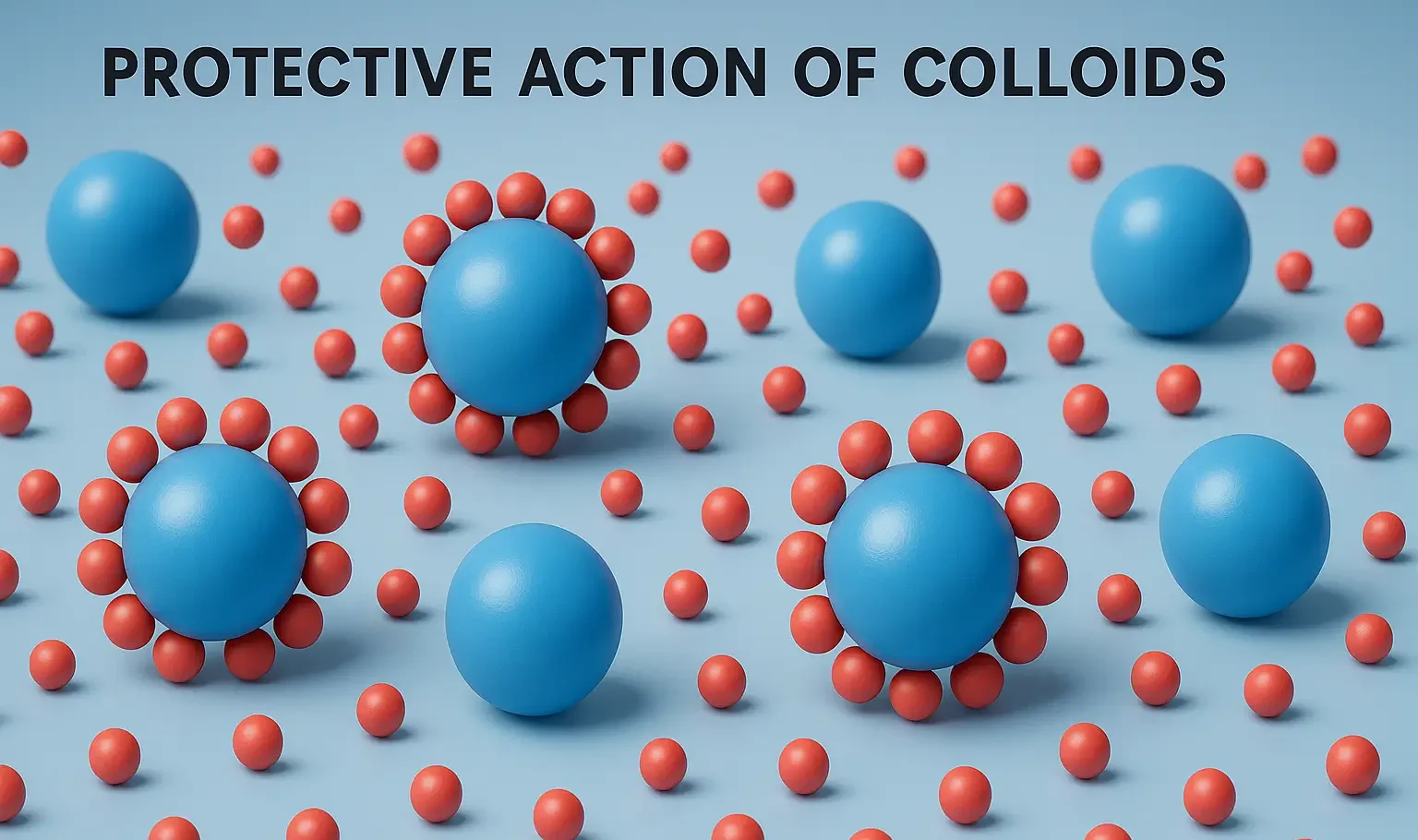
- Protective Action of Colloids prevents coagulation by stabilizing dispersed particles.
- It is vital in pharmaceuticals, food, and industrial formulations.
Definition:
- The ability of lyophilic colloids to protect lyophobic colloids from coagulation by electrolytes.
Mechanism:
- Lyophilic colloids form a protective layer around lyophobic particles, preventing them from aggregating.
Protective Colloid:
- A lyophilic colloid (such as gelatin or starch) forms a protective layer around lyophobic particles, preventing them from aggregating.
Advertisements
Gold Number (measure of protective ability):
- Defined as the minimum amount of protective colloid (mg) required to prevent coagulation of 10 mL of gold sol by 1 mL of 10
- Lower gold number = better protective action.
| Substance | Gold Number |
| Gelatin | 0.005 |
| Gum arabic | 0.1 |
| Egg albumin | 0.08 |
| Starch | 25 |
Applications:
- Stabilization of colloidal drug products.