-
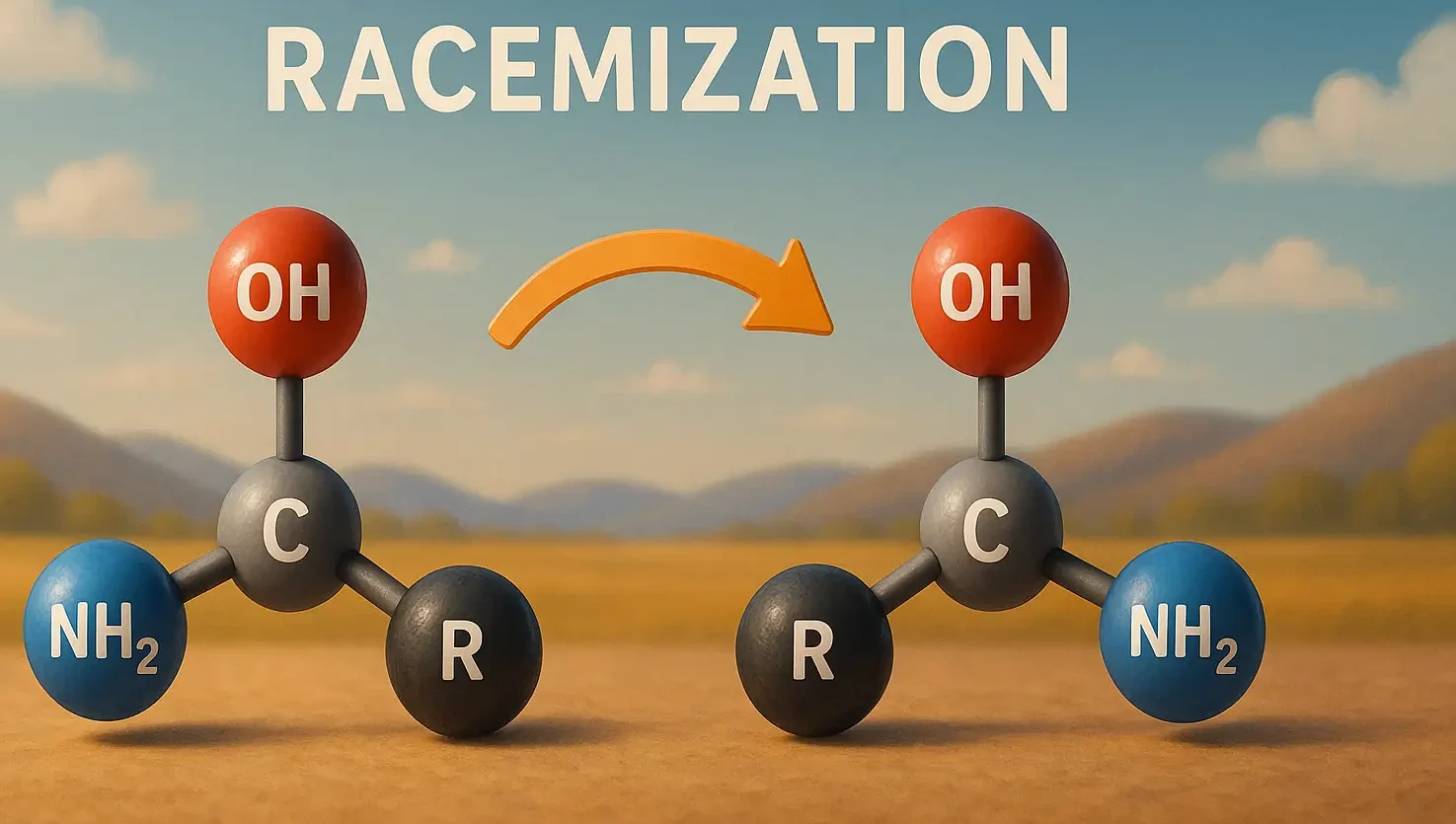
Definition of Racemization:
- Racemization is the interconversion of enantiomers (optical isomers) that can lead to changes in biological activity.
-
Mechanism:
- A chiral molecule can transform into its mirror-image isomer under certain conditions (pH, temperature, etc.).
Examples:
- Example Reaction (Racemization of Amino Acids):
- L-AminoAcid —[pH, temperature]→ D-AminoAcid
- Thalidomide: One enantiomer is therapeutic, while the other is teratogenic.
- Epinephrine: Converts to inactive isomers at higher pH.
Prevention Strategies of Racemization:
- Optimize pH and temperature during storage.
- Stabilize formulations using buffers.
- Choose enantiomerically pure drugs if racemization poses a risk.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos