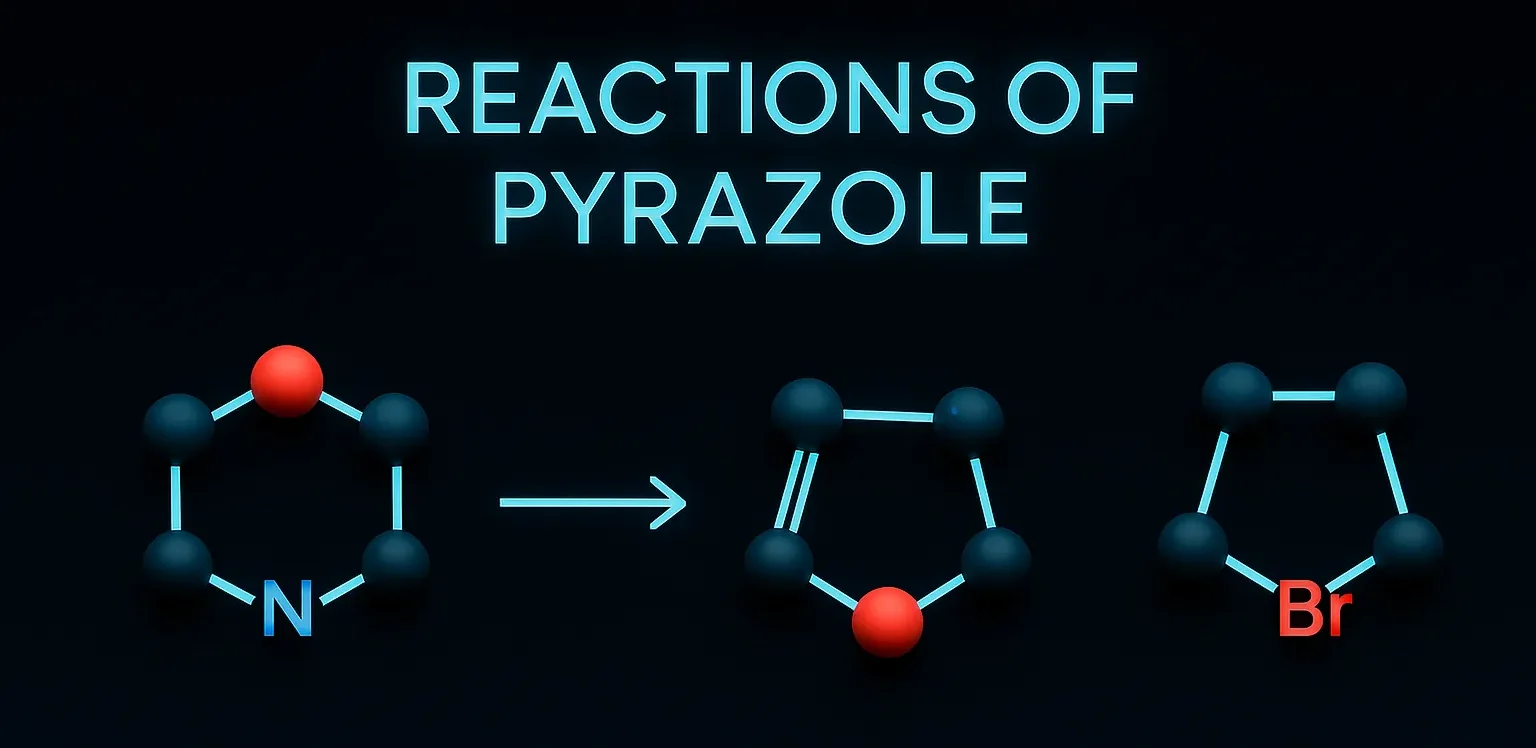
Reactions of Pyrazole mainly include electrophilic substitution at the 4-position and oxidation or reduction pathways.
Reactions of Pyrazole
-
Tautomerism:
- Pyrazole exhibits prototropic tautomerism between N-1 and N-2.
- 1H-pyrazole ⇌ 2H-pyrazole
- This affects reactivity at the nitrogen atoms and the electron density distribution on the ring.
- Pyrazole exhibits prototropic tautomerism between N-1 and N-2.
-
Electrophilic Substitution Reactions (EAS):
- Due to the electron-rich ring, EAS is favored at position-4 (C-4).
- Nitration:
- Reagents: HNO₃ + H₂SO₄
- Major product: 4-nitropyrazole
- Halogenation:
- Br₂/FeBr₃ → 4-bromopyrazole
- Sulfonation:
- Rare, only under harsh conditions.
- Nitration:
- Due to the electron-rich ring, EAS is favored at position-4 (C-4).
-
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions (NAS):
- Less common due to electron-rich ring.
- Possible if electron-withdrawing groups (e.g., NO₂) are at C-3 or C-5.
-
Metal Complex Formation:
- Pyrazole can coordinate metals through N-2.
- Often used in ligands like tris(pyrazolyl)borates for transition metal complexes.
-
Ring Functionalization:
- Lithiation at C-4 or C-5 followed by electrophile quench (e.g., CO₂, RCHO).
- C-alkylation possible via deprotonation with strong base (LDA).
-
Oxidation & Reduction:
- Not easily reduced due to aromaticity.
- Oxidation at N possible under strong conditions → N-oxides.
Advertisements